Digital PDS launch in Gujarat introduces a CBDC-based Public Distribution System to ensure transparent ration delivery under Minimum Government Maximum Governance. Learn key facts, exam relevance, FAQs and MCQs for UPSC, PSC, Banking and SSC exams.
Digital PDS Launched Under ‘Minimum Government, Maximum Governance’
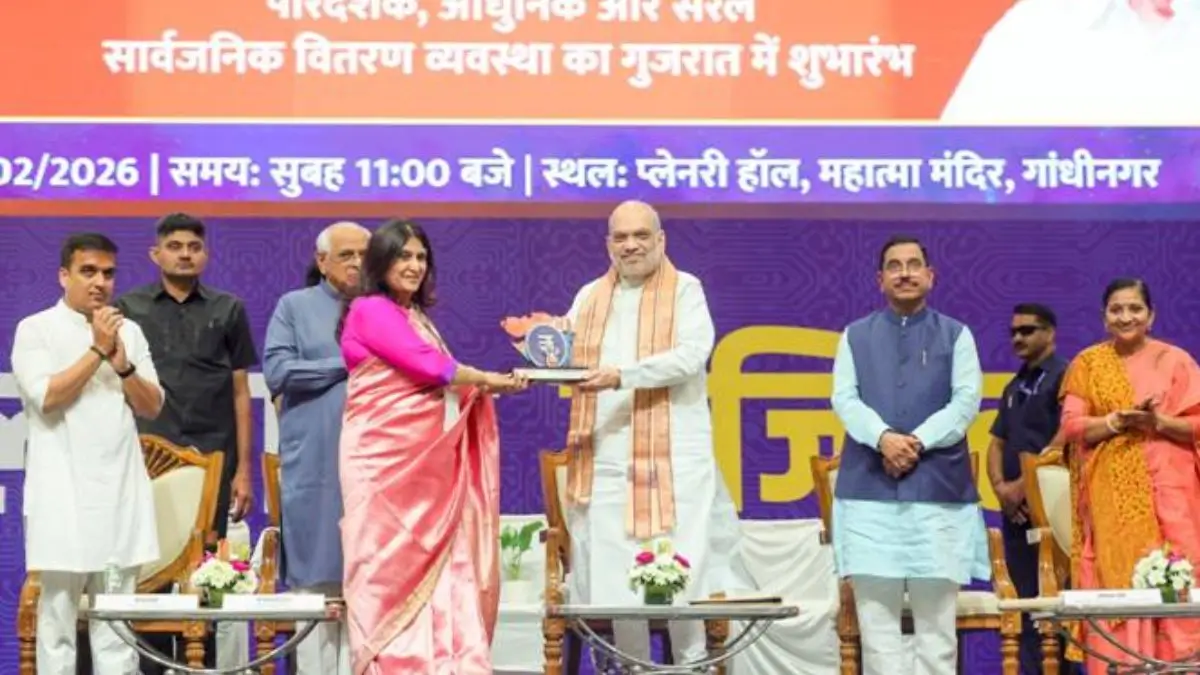
India has taken a major leap in the digital transformation of welfare delivery by launching the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)-based Public Distribution System (PDS). Union Home Minister Amit Shah inaugurated this innovative system in Gandhinagar, Gujarat as part of the government’s vision of “Minimum Government, Maximum Governance” – a flagship philosophy aimed at cutting red tape and delivering welfare with transparency, speed, and efficiency.
What is Digital PDS?
The Digital PDS integrates the use of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) – also known as the Digital Rupee – into India’s food security mechanism. Under this model:
- Digital tokens representing subsidised food grains are credited into beneficiaries’ wallets.
- These tokens specify the amount, type, and price of commodities eligible for distribution.
- The system is linked to existing Digital India infrastructure, ensuring secure transactions and real-time tracking.
How It Works
The new PDS replaces older paper-based and manual tracking systems with a digitally authenticated workflow:
- Beneficiaries access ration entitlements using their digital wallets.
- Smartphone users use QR codes, while feature phone users complete transactions via Aadhaar-linked OTP authentication.
- Automated machines called “Annapurna Grain ATMs” can dispense up to 25 kg of food grains in just 35 seconds, ensuring fast and precise delivery.
Importance of CBDC in Public Welfare
Integrating a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) into PDS is a first-of-its-kind reform in India. This approach is expected to:
✔ Reduce corruption and eliminate leakages in the ration supply chain.
✔ Enable real-time auditing, tracking, and accountability.
✔ Ensure beneficiaries receive exactly what they are entitled to, without middlemen interference.
Pilot Launch & Expansion
The pilot phase of Digital PDS begins in Gujarat, with the state’s food civil supplies department and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) working together on the launch. This initial rollout covers designated regions and will be evaluated before nationwide expansion over the next 3–4 years.
What Makes It Unique?
Unlike traditional welfare delivery systems in many Indian states, the Digital PDS:
- Removes lengthy paperwork and offline verification.
- Uses CBDC to secure and instantly confirm transactions.
- Builds upon India’s larger digital governance framework.
Why This News is Important for Competitive Exam Aspirants
The launch of the Digital PDS is significant for students preparing for government exams — especially PSC, UPSC (including IAS/IPS), banking, railways, defence, and teaching posts — because it reflects the Indian government’s policy priorities and digital governance reforms.
Relevance to Government Policies
This initiative directly aligns with the central government’s vision of “Minimum Government, Maximum Governance”, a recurring theme in recent policy frameworks aimed at reducing corruption, improving public service delivery, and enhancing administrative efficiency. Aspirants must be familiar with this concept as it often appears in GS Paper II (Governance) and Ethics sections.
Connection with Digital India & Welfare Reforms
The Digital PDS is an example of how the Digital India mission is linked with major welfare programmes such as the Public Distribution System, Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT), and digital identity tools like Aadhaar. Questions on integrating technology with social justice programs are common in both prelims and mains examinations.
Exam-Oriented Policy Perspective
Understanding Digital PDS helps exam-going students discuss:
- Modern tools used to eliminate leakages and corruption in welfare schemes.
- Government’s use of Central Bank Digital Currency for public service delivery.
- Broader changes in India’s approach to food security, transparency, and digital inclusion.
Historical Context: Evolution of PDS and Its Digital Transformation
The Public Distribution System (PDS) in India began shortly after independence as a means to ensure affordable food grains for poorer sections of society. Over the decades, the system expanded under national schemes like the Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS) and the National Food Security Act.
However, traditional PDS faced chronic issues such as:
- Leakages and diversion of food stocks.
- Fake ration cards benefiting ineligible persons.
- Delays and fraud in grain distribution.
Starting in the 2010s, the Indian government began digitising various components of PDS — from ePoS (electronic point of sale) machines to Aadhaar-linked authentication. This digitisation drive eliminated millions of fake ration cards, improved beneficiary targeting, and laid the groundwork for modern reforms.
The latest reform — using CBDC-based digital currency — marks a new stage in the digital evolution of PDS. It moves the system beyond authentication-only digitisation toward a fully digital, accountable, and transparent public welfare distribution model.
Key Takeaways from Digital PDS Launch
| S. No. | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1. | The Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)-based Public Distribution System was launched in Gandhinagar, Gujarat. |
| 2. | It uses digital rupee tokens for transparent, leak-proof ration delivery. |
| 3. | Integration with Digital India infrastructure enables real-time tracking and secure transactions. |
| 4. | Automated “Annapurna” machines can dispense 25 kg of grains quickly and accurately. |
| 5. | The pilot phase will expand nationwide over the next 3–4 years, strengthening welfare delivery. |
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions for Competitive Exams
1. What is the Digital PDS launched under “Minimum Government, Maximum Governance”?
Digital PDS is a CBDC-based Public Distribution System that uses the Central Bank Digital Currency (Digital Rupee) to distribute subsidised food grains to beneficiaries in a transparent and leak-proof manner.
2. Which state launched the pilot phase of the Digital PDS?
The pilot project was launched in Gujarat, specifically in Gandhinagar.
3. Who inaugurated the CBDC-based Public Distribution System?
The system was inaugurated by Amit Shah, the Union Home Minister of India.
4. What is CBDC?
CBDC stands for Central Bank Digital Currency, which is the digital form of sovereign currency issued by a central bank. In India, it is issued by the Reserve Bank of India.
5. Under which broader governance philosophy was this initiative launched?
It aligns with the government’s vision of Minimum Government, Maximum Governance, which focuses on efficiency, transparency, and reduced bureaucratic intervention.
6. What is the objective of integrating CBDC into PDS?
The main objectives are:
- Elimination of leakages
- Reduction of corruption
- Real-time transaction tracking
- Enhanced beneficiary authentication
7. Which Act governs India’s food security system?
India’s food security mechanism is governed by the National Food Security Act.
8. How does Digital PDS benefit competitive exam aspirants?
It is important for UPSC GS Paper II (Governance), Banking Awareness, State PSC, SSC, Railways, Defence Exams, and other competitive examinations where questions on digital governance, welfare schemes, and economic reforms are common.
9. What technological tools are used in Digital PDS?
- Digital Rupee (CBDC)
- Aadhaar-based authentication
- QR codes
- OTP verification
- Automated grain dispensing machines
10. How is this reform linked to Digital India?
The initiative strengthens the objectives of the Digital India programme by integrating technology with public welfare distribution.
Some Important Current Affairs Links