India animal blood bank guidelines introduced to standardize veterinary blood transfusion, donor selection, and ethical practices, ensuring animal welfare and public health safety.
India Launches First-Ever National Guidelines for Animal Blood Transfusion and Blood Banks
Introduction
In a significant advancement for veterinary healthcare, India has introduced its first-ever national guidelines for animal blood transfusion and blood banks. Released by the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying, these guidelines aim to standardize and regulate blood transfusion practices for animals across the country.
Need for Standardization
Prior to these guidelines, animal blood transfusions in India were often conducted in emergency situations without standardized protocols. This lack of uniformity posed risks such as incompatible transfusions and inadequate donor screening, leading to potential health complications for animals. The introduction of these guidelines addresses these concerns by establishing a structured framework for blood donation, storage, and transfusion procedures.
Key Provisions of the Guidelines
1. Donor Selection and Eligibility
The guidelines specify criteria for selecting animal blood donors, including health status, vaccination records, and age. Only healthy animals that meet these criteria are eligible to donate blood, ensuring the safety and efficacy of transfusions.
2. Mandatory Blood Typing and Cross-Matching
To prevent adverse reactions, the guidelines mandate blood typing and cross-matching for all transfusions. This ensures compatibility between donor and recipient blood, reducing the risk of transfusion-related complications.
3. Establishment of Veterinary Blood Banks
The guidelines call for the establishment of state-regulated veterinary blood banks equipped with biosafety-compliant infrastructure. These facilities will serve as centralized locations for blood collection, processing, and storage, facilitating efficient management of animal blood resources.
4. Voluntary and Informed Donor Participation
Emphasizing ethical practices, the guidelines promote voluntary, non-remunerated blood donations. A Donor Rights Charter has been introduced to ensure informed consent and the welfare of donor animals.
5. Integration of One Health Approach
Recognizing the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health, the guidelines integrate the One Health approach. This holistic perspective aims to manage zoonotic risks and promote overall public health.
Implementation and Future Directions
The implementation of these guidelines involves the creation of a National Veterinary Blood Bank Network (NVBBN), featuring digital registries, real-time inventory tracking, and an emergency helpline. Training modules for veterinary students and professionals will be incorporated to ensure adherence to these standards. Future innovations encouraged under the guidelines include mobile blood collection units, preservation techniques for rare blood types, and mobile applications for donor-recipient matching.
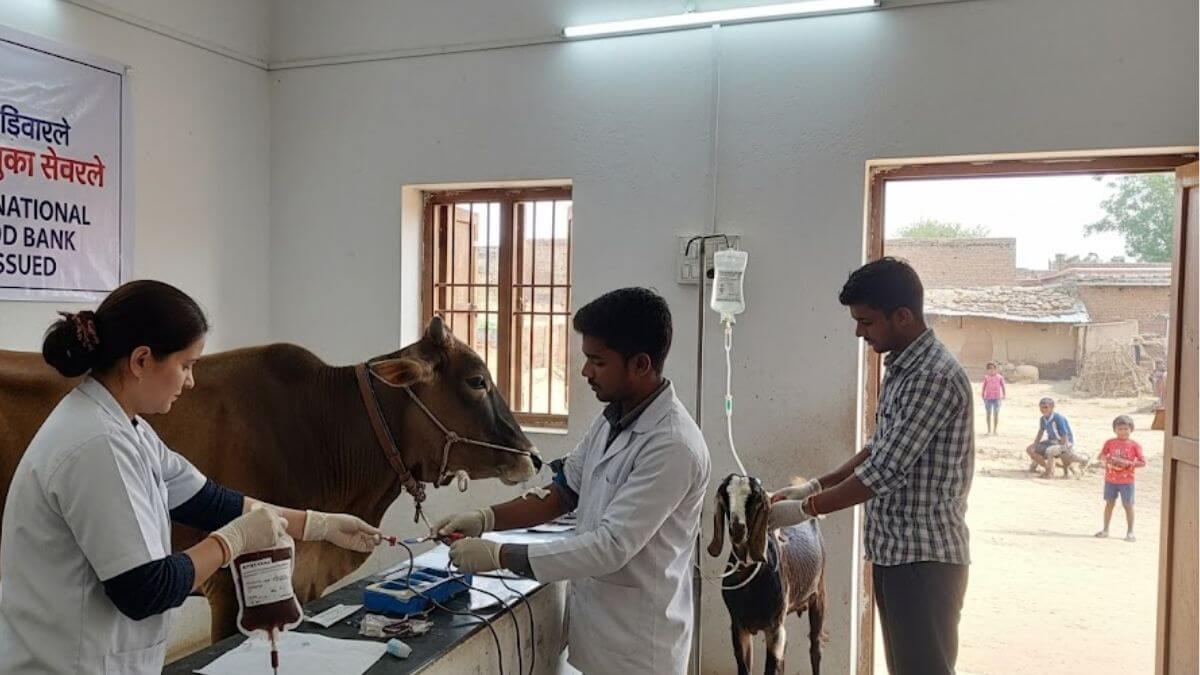
Why This News Is Important
Enhancing Animal Welfare
The introduction of standardized blood transfusion practices ensures that animals receive safe and effective care, improving overall animal welfare.
Strengthening Veterinary Healthcare Infrastructure
The establishment of state-regulated veterinary blood banks enhances the infrastructure for animal healthcare, facilitating better management of blood resources.
Promoting Ethical Practices
The emphasis on voluntary and informed donor participation promotes ethical practices in veterinary care, safeguarding the rights and welfare of animals.
Aligning with Global Standards
By adopting international best practices, India aligns its veterinary healthcare standards with global norms, fostering credibility and trust in its veterinary services.
Integrating One Health Approach
The integration of the One Health approach addresses the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health, promoting comprehensive public health strategies.
Historical Context: Evolution of Animal Blood Transfusion in India
Historically, animal blood transfusions in India were performed in emergency situations without standardized protocols. This lack of uniformity posed risks and highlighted the need for a structured framework. The development of these guidelines marks a significant milestone in the evolution of veterinary healthcare in India, reflecting a commitment to improving animal welfare and healthcare standards.
Key Takeaways from “India Launches First-Ever National Guidelines for Animal Blood Transfusion and Blood Banks”
| S.No. | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | Introduction of National Guidelines: India has released its first-ever national guidelines for animal blood transfusion and blood banks. |
| 2 | Mandatory Blood Typing and Cross-Matching: The guidelines mandate blood typing and cross-matching to prevent adverse reactions. |
| 3 | Establishment of Veterinary Blood Banks: State-regulated veterinary blood banks with biosafety-compliant infrastructure will be established. |
| 4 | Promotion of Voluntary Donations: The guidelines emphasize voluntary, non-remunerated blood donations with informed consent through a Donor Rights Charter. |
| 5 | Integration of One Health Approach: The guidelines integrate the One Health approach to manage zoonotic risks and promote public health. |
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the newly introduced guidelines for animal blood banks in India?
A1. India has launched its first-ever national guidelines for animal blood transfusion and blood banks to standardize donor selection, blood typing, transfusion protocols, and ethical practices for animals.
Q2. Which government body released the guidelines?
A2. The Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD), under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying, issued the guidelines.
Q3. Why is blood typing and cross-matching mandatory for animals?
A3. Blood typing and cross-matching prevent transfusion-related complications and ensure compatibility between donor and recipient animals.
Q4. What is the role of veterinary blood banks under the new guidelines?
A4. Veterinary blood banks will serve as centralized facilities for blood collection, processing, storage, and emergency supply management in a biosafety-compliant manner.
Q5. How do the guidelines ensure ethical practices for animal donors?
A5. The guidelines emphasize voluntary, non-remunerated blood donations and include a Donor Rights Charter to protect the welfare of donor animals.
Q6. What is the One Health approach mentioned in the guidelines?
A6. The One Health approach recognizes the connection between human, animal, and environmental health, helping prevent zoonotic diseases and promote public health.
Q7. How will these guidelines benefit veterinary healthcare in India?
A7. They will enhance infrastructure, ensure safe transfusions, promote ethical practices, and align Indian veterinary standards with global best practices.
Some Important Current Affairs Links