ITER: The Future of Fusion Energy
Introduction to ITER and Fusion Energy
The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) is one of the most ambitious energy projects in the world. Located in France, this multinational initiative aims to develop nuclear fusion as a viable and sustainable energy source. Nuclear fusion, the process that powers the sun, has long been considered the “holy grail” of clean energy due to its potential for unlimited, safe, and eco-friendly electricity generation.
Objectives of the ITER Project
The ITER project is designed to demonstrate the feasibility of fusion energy by creating plasma conditions similar to those found in the sun. The main goals of ITER include:
- Producing 500 megawatts of fusion power from a 50-megawatt input, showcasing its efficiency.
- Testing and advancing fusion technologies for future commercial reactors.
- Providing insights into the sustainability and scalability of fusion power.
How ITER Works: The Science Behind It
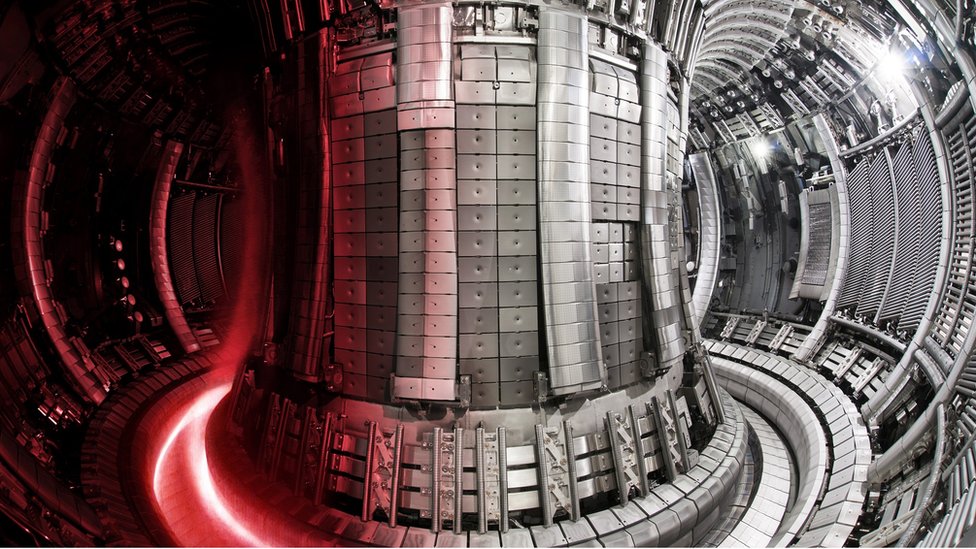
The core of ITER is a Tokamak reactor, a device that uses powerful magnetic fields to confine and heat plasma. The reactor will use hydrogen isotopes—deuterium and tritium—to initiate fusion reactions. When these isotopes collide at high temperatures, they fuse into helium and release massive amounts of energy. Unlike nuclear fission, which splits atoms and produces long-lasting radioactive waste, fusion energy is much safer and generates minimal waste.
Global Collaboration and Investment
ITER is a joint initiative involving 35 countries, including India, the United States, China, Russia, the European Union, Japan, and South Korea. India, as a key partner, contributes to various components, including superconducting magnets and cryostat systems. The project, with an estimated cost of over $20 billion, represents one of the largest global scientific collaborations in history.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its promising potential, ITER faces several challenges, including:
- High costs and extended timelines for construction and testing.
- Complex engineering requirements for sustaining high-temperature plasma.
- The need for advanced materials to withstand extreme fusion conditions.
However, once operational, ITER could revolutionize global energy systems, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.

Why This News is Important
Potential for a Clean Energy Future
The ITER project holds significant importance as it could be a game-changer in clean energy. With growing concerns over climate change and fossil fuel depletion, fusion energy offers a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative.
Global Scientific and Economic Impact
ITER is one of the largest international collaborations in science and engineering. Its success could drive further investments in fusion energy, creating economic and employment opportunities worldwide.
India’s Role in the ITER Project
India plays a crucial role in ITER by contributing key technological components. This involvement enhances India’s scientific reputation and strengthens its expertise in nuclear energy.
Historical Context: The Journey of Fusion Research
The concept of nuclear fusion dates back to the early 20th century when scientists first understood how the sun generates energy. The first experimental fusion reactions were conducted in the 1950s, leading to the development of Tokamak reactors in the 1960s. The ITER project was formally established in 1985 as a global initiative to advance fusion technology. Over the years, numerous breakthroughs in plasma confinement and superconducting materials have paved the way for ITER’s construction and future operation.
Key Takeaways from ITER: The Future of Fusion Energy
| S.No | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | ITER is a multinational project aimed at developing nuclear fusion as a clean energy source. |
| 2 | The Tokamak reactor in ITER will generate 500 MW of power using hydrogen isotopes. |
| 3 | Fusion energy produces minimal radioactive waste and has the potential to replace fossil fuels. |
| 4 | India is a key contributor to ITER, providing advanced technological components. |
| 5 | The success of ITER could revolutionize global energy production and sustainability. |
Important FAQs for Students from this News
What is ITER?
ITER (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor) is a multinational nuclear fusion research project aimed at developing clean and sustainable energy.
How does nuclear fusion differ from nuclear fission?
Fusion combines light atoms (hydrogen isotopes) to release energy, whereas fission splits heavy atoms (uranium/plutonium), producing more radioactive waste.
Why is ITER important for global energy security?
ITER aims to generate unlimited, carbon-free energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and helping combat climate change.
What is India’s role in the ITER project?
India is one of the key contributors to ITER, providing essential components like superconducting magnets and cryostat systems.
When is ITER expected to become operational?
ITER’s first plasma operations are expected by the late 2020s, with full-scale experiments planned for the 2030s.
Some Important Current Affairs Links