Understanding ISDN: Integrated Services Digital Network
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a telecommunications standard for digital transmission of voice, data, and video over traditional circuits. Initially developed in the 1980s, ISDN aimed to replace analog systems by allowing multiple services to be delivered over a single line. This technology played a crucial role in the transition to digital communication, paving the way for modern telecommunications systems.
Key Features of ISDN
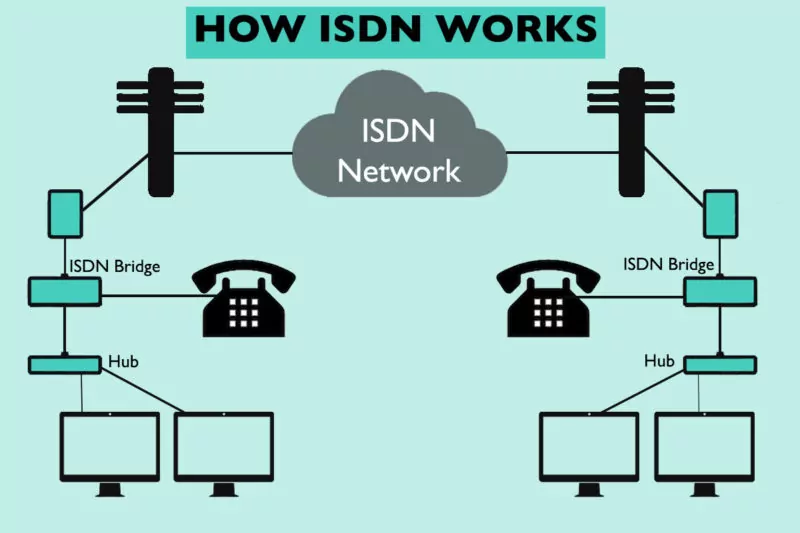
ISDN integrates various services such as voice, video, and data, enabling users to conduct simultaneous communications. It operates using two main types of channels: B channels (Bearer) for voice and data, and D channels (Delta) for signaling and control. This structure allows for efficient bandwidth utilization, offering data rates up to 128 Kbps with multiple B channels combined.
ISDN offers two primary interfaces: BRI (Basic Rate Interface) and PRI (Primary Rate Interface). BRI is designed for small-scale applications, providing two B channels and one D channel, ideal for home and small office use. Conversely, PRI is intended for larger organizations, supporting up to 30 B channels and one D channel, making it suitable for businesses requiring high-capacity communication.
Applications of ISDN
The versatility of ISDN has led to its widespread use in various fields. In telephony, ISDN provides high-quality voice services, while in video conferencing, it enables seamless communication with minimal latency. Additionally, ISDN is employed in broadcasting, allowing live video transmission from remote locations to studios, and in data transmission, offering reliable and fast connections for corporate networks.
Why This News is Important
Significance of ISDN in Modern Communication
ISDN represents a significant advancement in telecommunications, as it bridges the gap between traditional analog systems and modern digital technologies. Its ability to transmit multiple types of data over a single line has laid the groundwork for contemporary services like VoIP and broadband internet, highlighting its relevance in today’s communication landscape.
Impact on Telecommunication Infrastructure
The deployment of ISDN has influenced telecommunication infrastructure worldwide, prompting service providers to upgrade their networks. This upgrade has not only enhanced communication quality but also increased service reliability, making ISDN a vital component of the global telecommunication framework.
Relevance in Government and Education
For students preparing for government exams, understanding ISDN is crucial, particularly in fields related to telecommunications and information technology. Knowledge of ISDN can aid in comprehending the evolution of communication technologies and their impact on various sectors, including education, public service, and law enforcement.
Historical Context
ISDN was introduced in the late 1980s as a response to the growing demand for high-quality voice and data communication. Its development was part of a broader trend towards digitalization in telecommunications, driven by advancements in technology and the need for more efficient communication systems. Over the years, ISDN has evolved, influencing the design of modern communication protocols and serving as a precursor to contemporary technologies such as broadband and mobile communication.
Key Takeaways from “Understanding ISDN”
| Serial Number | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | ISDN stands for Integrated Services Digital Network. |
| 2 | It enables simultaneous transmission of voice, data, and video. |
| 3 | ISDN operates using two types of channels: B channels for data and D channels for signaling. |
| 4 | The two main interfaces of ISDN are BRI and PRI, serving different scale applications. |
| 5 | ISDN significantly influenced the evolution of modern telecommunications. |
Important FAQs for Students from this News
Q1: What does ISDN stand for?
A1: ISDN stands for Integrated Services Digital Network, a standard for digital transmission of voice, data, and video.
Q2: What are the two main types of ISDN interfaces?
A2: The two main types of ISDN interfaces are Basic Rate Interface (BRI) and Primary Rate Interface (PRI).
Q3: What is the maximum data rate supported by ISDN?
A3: ISDN can support data rates of up to 128 Kbps when combining multiple B channels.
Q4: How does ISDN improve communication quality compared to analog systems?
A4: ISDN provides higher quality, more reliable transmission of voice and data by reducing latency and interference.
Q5: In what applications is ISDN commonly used?
A5: ISDN is commonly used in telephony, video conferencing, broadcasting, and data transmission for corporate networks.
Some Important Current Affairs Links