Punjab Bharat Net Scheme: Punjab becomes the first state to implement the amended Bharat Net Scheme statewide, enhancing rural broadband connectivity, digital services, and border monitoring.
Punjab Becomes First State to Implement Amended Bharat Net Scheme Statewide
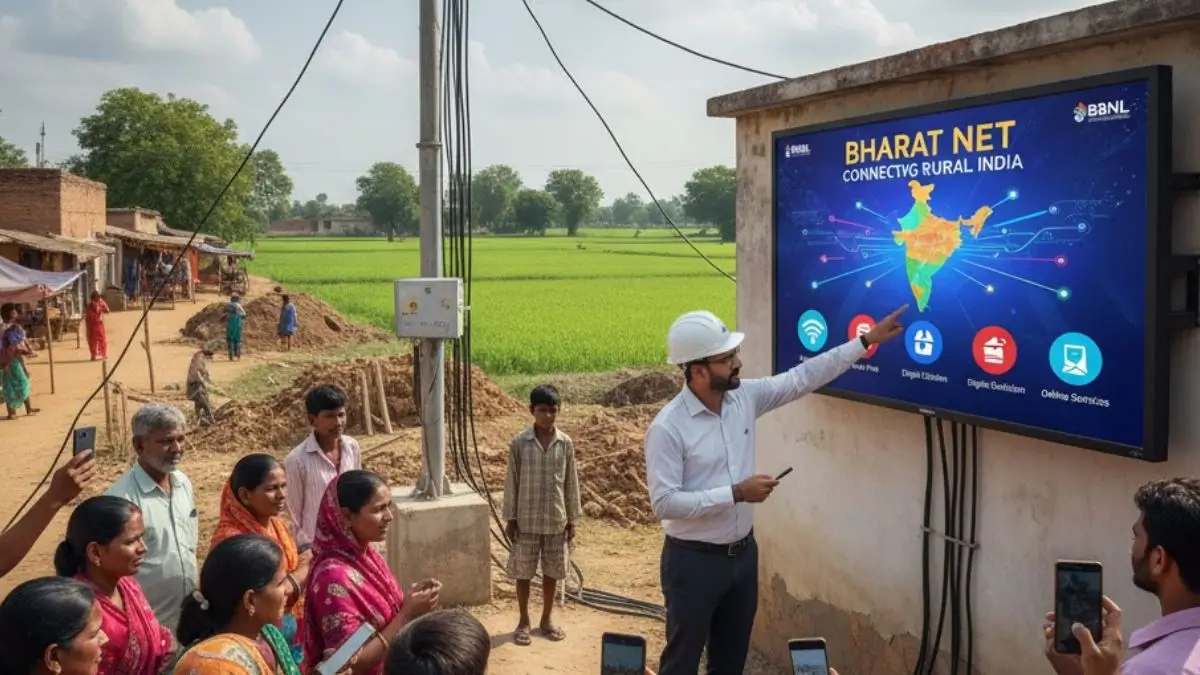
Punjab has made a landmark achievement by becoming the first state in India to fully implement the amended Bharat Net Scheme across its entire territory.This ambitious scheme brings high-speed broadband connectivity to rural areas, enabling not only improved internet access but also enhanced e-governance, e-health services, and real-time monitoring of border regions.
Implementation and Recognition
The Chief Secretary of Punjab, KAP Sinha, received an award from Ajay Kumar Kararha, CGM of BSNL Punjab Circle, in recognition of the state’s exemplary execution of the amended Bharat Net Scheme. Under this rollout, broadband services now reach 43 shadow areas—remote or underserved villages—and just one village remains uncovered, with expectations of full statewide coverage by the end of November 2025.
Strengthening Digital Infrastructure
One of the most significant advantages of the scheme’s pan-state implementation is the ability to monitor border regions live from anywhere in the country, thanks to robust fiber-optic infrastructure. This infrastructure also enhances delivery of digital public services, especially in rural Punjab: e-governance, e-health, and digital education will benefit significantly.
A Scalable Model for Other States
Punjab’s success is not just a regional win — it sets a template for other states to follow. The model demonstrates how to integrate a large-scale fiber-optic network, ensure last-mile connectivity, and leverage central monitoring (via the S-NOC / state network operations centre) for better governance and digital inclusion.
Static and Technical Facts
- Punjab is the first Indian state to implement the amended Bharat Net Scheme statewide.
- Nearly all villages are covered; only one remains.
- 43 “shadow areas” are already connected.
- The amended Bharat Net programme has a design cost of around ₹ 1,39,579 crore and includes key technical components like OFC (optical fiber) ring topology, IP‑MPLS network architecture, last‑mile connectivity, central network monitoring (CNOC), and a ten-year operation & maintenance plan.
Why This News Is Important
Significance for Rural Connectivity
This development is crucial because it bridges the digital divide in Punjab’s rural landscape. By bringing broadband to remote Gram Panchayats and “shadow areas,” the initiative empowers rural citizens with access to education, health services, and government schemes via digital platforms. This aligns with national priorities under Digital India.
National Security & Border Monitoring
The ability to monitor border areas live from anywhere in India is a strategic gain. Punjab shares a border with Pakistan, and real-time connectivity can significantly strengthen surveillance, coordination, and disaster-response infrastructure, making governance more agile and responsive.
Governance and Public Service Delivery
With broadband in almost every village, e-governance and e-health services become more effective and widespread. This opens the door for telemedicine, digital education, and online administrative services, improving efficiency and reducing bureaucratic delays.
Model for Other States
Punjab’s successful implementation can serve as a blueprint for other states, especially those with difficult terrain or remote populations. Governments can replicate its model to achieve statewide broadband rollout while leveraging centralized monitoring and robust infrastructure.
Exam Relevance
For students preparing for government exams (Teachers, UPSC, State PSCs, Railways, etc.), this news is highly relevant under the ‘Schemes and Initiatives’ portion of the syllabus. Questions may be asked about the Bharat Net scheme, its objectives, technical components, and states that have successfully implemented it.
Historical Context
Origins of the Bharat Net Scheme
Bharat Net (formerly known as National Optical Fibre Network – NOFN) was launched as a flagship program by the Government of India to bring broadband connectivity to rural India. The original scheme aimed to connect all Gram Panchayats via high-speed optical fiber.
Evolution to the Amended Bharat Net
Over time, it became clear that the original plan needed stronger backbone infrastructure, better monitoring, and more sustainable maintenance. Thus, the amended Bharat Net Scheme was introduced, with technical upgrades such as a ring topology of fiber, IP-MPLS architecture, and a central Network Operations Center (CNOC) to monitor the network.
Funding and Scale
The updated Bharat Net project is massive. With a design cost of approximately ₹ 1,39,579 crore, the scheme targets high-speed broadband for all inhabited villages and includes a 10-year operations & maintenance plan.
Implementation Challenges & Progress
Rolling out fiber in remote and rural areas has always been challenging due to terrain, right-of-way issues, and funding. But successful state-level implementations like Punjab’s are critical milestones. They show that with coordinated state and central efforts, even border and shadow regions can be digitally integrated.
Key Takeaways from Punjab’s Bharat Net Achievement
| No. | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | Punjab is the first state in India to implement the amended Bharat Net Scheme across its entire territory. |
| 2 | 43 “shadow areas” in Punjab are now connected, with only one village remaining for full coverage. |
| 3 | The scheme’s infrastructure enables live monitoring of border regions from anywhere in the country. |
| 4 | Implementation will help deliver e-governance, e-health, and digital education services in rural Punjab. |
| 5 | Punjab’s rollout is a model for other states to follow for last-mile broadband, centralized monitoring, and digital inclusion. |
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the Bharat Net Scheme?
The Bharat Net Scheme is a flagship initiative by the Government of India to provide high-speed broadband connectivity to all Gram Panchayats and rural areas, aiming to bridge the digital divide and promote digital inclusion.
2. What is the amended Bharat Net Scheme?
The amended Bharat Net Scheme includes technical upgrades, such as ring topology fiber networks, IP-MPLS architecture, last-mile connectivity, and centralized monitoring through CNOC, making the network more robust and manageable.
3. Why is Punjab’s implementation significant?
Punjab is the first Indian state to implement the amended Bharat Net Scheme statewide, covering almost all villages, including 43 “shadow areas.” This ensures digital inclusion, border monitoring, and e-governance benefits.
4. How does this scheme benefit border security?
The fiber-optic network enables live monitoring of border regions from anywhere in India, improving surveillance, disaster response, and national security.
5. What services will benefit from this broadband connectivity?
Services like e-governance, telemedicine, digital education, online administrative services, and citizen grievance redressal will be more accessible and efficient in rural areas.
6. What is the total cost of the amended Bharat Net Scheme?
The amended scheme has a design cost of approximately ₹1,39,579 crore and includes a 10-year operation & maintenance plan.
7. Can other states replicate Punjab’s model?
Yes, Punjab’s implementation serves as a blueprint for other states, demonstrating scalable and sustainable broadband deployment in rural and remote regions.
8. When is Punjab expected to achieve full statewide coverage?
Punjab is expected to achieve full broadband coverage by the end of November 2025, covering the one remaining village.
Some Important Current Affairs Links