Madhya Pradesh’s Kuno National Park: A Home to Asiatic Lions
Madhya Pradesh is known for its rich wildlife, and one of the most important and celebrated attractions in the state is the Kuno National Park, which has gained international attention due to its successful efforts to reintroduce the Asiatic lions. This landmark initiative is not only vital for the preservation of these majestic creatures but also plays a crucial role in the biodiversity of the region. In this article, we will explore the significance of Kuno National Park, its role in Asiatic lion conservation, and its potential impact on Madhya Pradesh’s tourism and wildlife conservation efforts.
The Importance of Kuno National Park
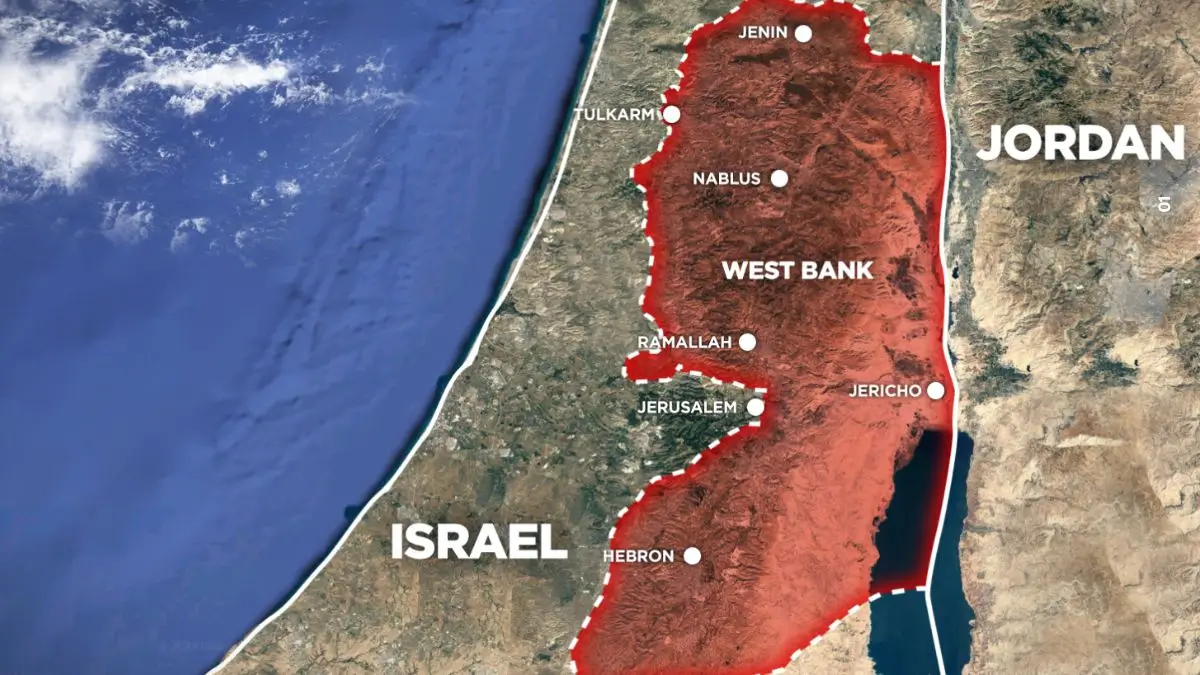
Kuno National Park, located in the northern part of Madhya Pradesh, is an ecological haven spread across an area of over 750 square kilometers. Established in 1981, it initially aimed to protect the unique ecosystem of the region. However, the park’s prominence increased after it became a key site for the reintroduction of Asiatic lions that once roamed freely across India but faced a severe decline in population due to habitat loss, poaching, and competition with other species.
Reintroduction of Asiatic Lions
The Asiatic lion, a subspecies of the African lion, once thrived in the forests and grasslands of India. Today, the Gir National Park in Gujarat is the only home of the Asiatic lion in the wild. However, the Indian government has been working to diversify the population of these endangered lions to other regions, including Madhya Pradesh, to ensure their long-term survival. Kuno National Park has been identified as an ideal location for the reintroduction of these lions due to its suitable habitat, prey base, and low human disturbance.
The project to bring Asiatic lions to Kuno was first conceptualized in the 1990s, with the plan being formally approved in 2013. Following several years of preparation, the first batch of Asiatic lions was introduced to the park in 2020, marking a milestone in conservation efforts for this endangered species. The reintroduction aims not only to preserve the species but also to spread the population to a broader geographic area, reducing the risk of a potential disease outbreak or environmental disaster affecting the entire population.
Ecological Significance of Asiatic Lions
As top predators, Asiatic lions play a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance of their habitat. By controlling the populations of herbivores, these lions help maintain the health of the park’s grasslands and forests. Their presence is expected to have a positive cascading effect on the ecosystem, benefiting other species of flora and fauna that depend on a balanced food chain. Furthermore, the successful conservation of Asiatic lions has raised awareness about the need for habitat preservation and sustainable wildlife management across India.

Why This News is Important
Contribution to Wildlife Conservation in India
The reintroduction of Asiatic lions to Kuno National Park is a major achievement for wildlife conservation in India. This move marks a significant step in diversifying the habitat of the Asiatic lion, reducing the risk of extinction, and ensuring the species’ survival for future generations. India’s commitment to preserving endangered species like the Asiatic lion showcases the country’s growing focus on biodiversity conservation and ecosystem restoration.
Boosting Madhya Pradesh’s Tourism Industry
The successful relocation of Asiatic lions has the potential to significantly boost tourism in Madhya Pradesh. The state, which is already home to several other prominent wildlife reserves such as Kanha National Park and Bandhavgarh National Park, now has a unique selling point to attract eco-tourists and wildlife enthusiasts from across the globe. The presence of the Asiatic lions in the park will further enhance the state’s reputation as a prime destination for wildlife tourism.
Enhancing Global Recognition of India’s Conservation Efforts
India’s wildlife conservation strategies, especially the efforts to reintroduce the Asiatic lion into its natural habitats, have been receiving global recognition. This successful initiative underscores India’s dedication to protecting its natural heritage and addressing biodiversity challenges. It also serves as a model for other countries engaged in wildlife preservation projects and highlights India’s role as a leader in the global conservation movement.
Historical Context: The Asiatic Lion’s Journey
The Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica), once found across the Indian subcontinent and the Middle East, saw its population dwindle due to hunting, habitat loss, and conflict with humans. By the end of the 19th century, these lions were on the brink of extinction, with only a small population surviving in the Gir Forest of Gujarat, India.
In the early 20th century, conservation efforts began in the Gir Forest, and these efforts led to a slow recovery of the Asiatic lion population. The 1990s marked a new phase in conservation, with discussions about relocating some of the lions to other suitable areas to ensure a healthy, stable population. Kuno National Park was identified as a suitable site due to its topography and prey base, and thus began the long process of preparing the park for the lions’ arrival.
Over the years, the Indian government has invested significant resources into the conservation of Asiatic lions, and the success of Kuno National Park’s lion reintroduction project is a testament to these efforts. The project also plays a crucial role in restoring the ecological balance in the region and contributing to global conservation goals.
Key Takeaways from “Madhya Pradesh’s Kuno National Park and Asiatic Lions”
| Serial Number | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh is a crucial site for the reintroduction of Asiatic lions. |
| 2 | The Asiatic lion was once widespread across India, but now only survives in the Gir National Park in Gujarat. |
| 3 | The successful relocation of Asiatic lions to Kuno National Park marks a major achievement in wildlife conservation. |
| 4 | Asiatic lions are vital for maintaining ecological balance by controlling herbivore populations. |
| 5 | The introduction of Asiatic lions to Kuno is expected to boost tourism and raise global awareness of India’s conservation efforts. |
Important FAQs for Students from this News
What is the significance of Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh?
- Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh is renowned for its efforts to reintroduce Asiatic lions, an endangered species. The park plays a vital role in conserving these lions and maintaining the ecological balance in the region.
Why was Kuno National Park selected for the reintroduction of Asiatic lions?
- Kuno National Park was chosen due to its suitable habitat, which includes vast grasslands and forests, a diverse prey base, and low human disturbance, making it an ideal location for the Asiatic lions to thrive.
When were the first Asiatic lions reintroduced to Kuno National Park?
- The first batch of Asiatic lions was reintroduced to Kuno National Park in 2020, marking a major milestone in conservation efforts.
How does the reintroduction of Asiatic lions impact the local ecosystem?
- Asiatic lions are apex predators, and their presence helps control herbivore populations, which in turn maintains the health of the ecosystem. Their reintroduction has positive effects on the biodiversity of the park.
What is the historical background of the Asiatic lion?
- Asiatic lions were once widespread in India but faced a sharp decline in population due to hunting and habitat loss. Today, they are primarily found in the Gir National Park of Gujarat, with efforts being made to reintroduce them to other regions like Kuno.
Some Important Current Affairs Links