Three Least Literate States of India
Introduction
India, known for its diverse and vibrant culture, faces significant challenges in education, particularly in its least literate states. The recent report on literacy rates highlights the educational disparities among states, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions. This article delves into the details of the three least literate states in India, exploring the factors contributing to their low literacy rates and the implications for national development.
Overview of Literacy Rates
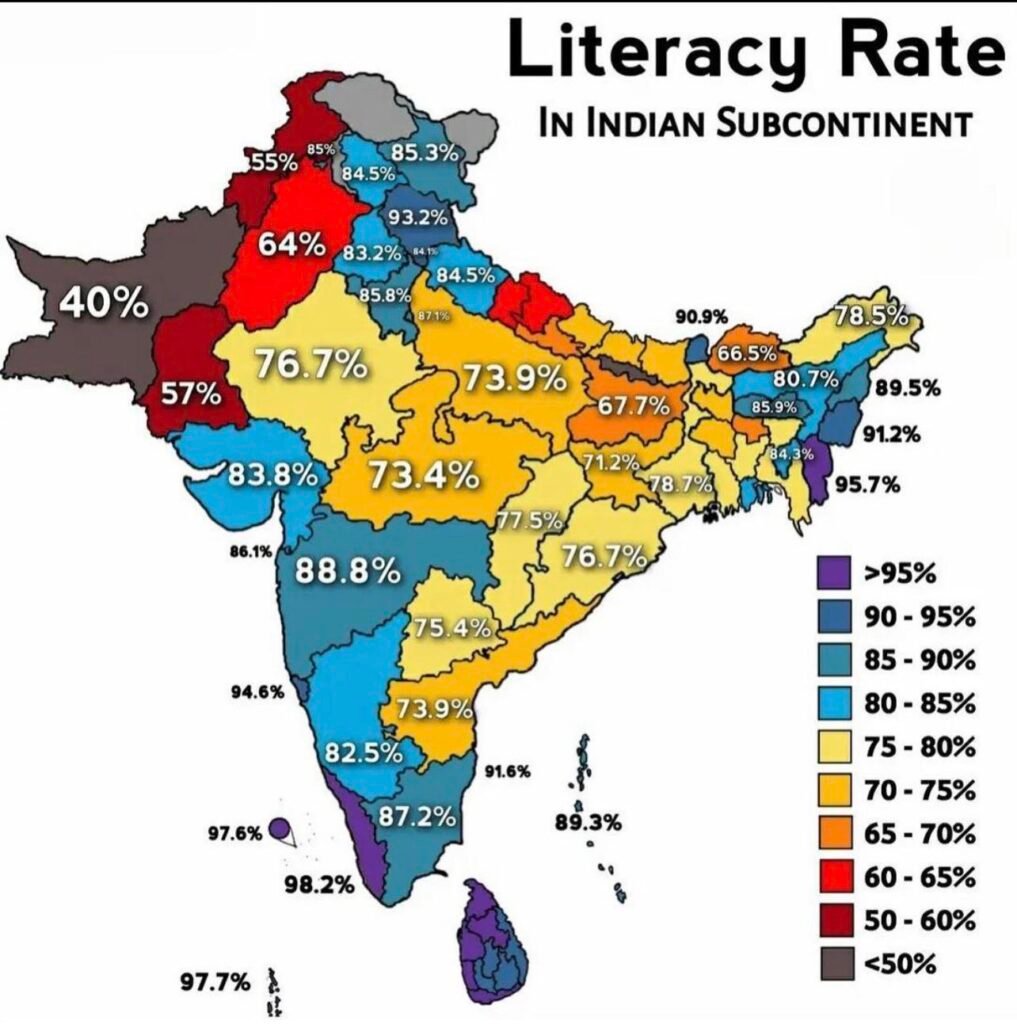
According to the latest data, the three least literate states in India are Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Arunachal Pradesh. These states exhibit considerably lower literacy rates compared to the national average. For instance, Bihar’s literacy rate stands at approximately 70%, while Uttar Pradesh and Arunachal Pradesh have rates of around 73% and 66%, respectively. This disparity underscores the urgent need for enhanced educational policies and programs in these regions.
Contributing Factors
Several factors contribute to the low literacy rates in these states. Socio-economic challenges, such as poverty and lack of infrastructure, play a significant role. In rural areas, limited access to quality education and resources further exacerbates the problem. Additionally, cultural and social barriers, including gender inequality and traditional practices, hinder educational progress. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach, involving both government and community efforts.
Government Initiatives
The Indian government has launched various initiatives to improve literacy rates, including the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) and the Beti Bachao Beti Padhao scheme. These programs aim to enhance educational infrastructure, promote gender equality, and increase enrollment rates. Despite these efforts, the implementation and impact in the least literate states have been limited, highlighting the need for more focused strategies and resource allocation.
Future Outlook
The future of literacy in these states hinges on the effectiveness of ongoing and new educational reforms. Strengthening school infrastructure, improving teacher training, and engaging communities in educational initiatives are crucial steps. By addressing the root causes of low literacy rates and implementing comprehensive solutions, there is hope for significant progress in these regions.
Why This News is Important
Addressing Educational Disparities
Understanding the literacy rates in the least literate states of India is crucial for addressing educational disparities. These states lag behind in terms of educational attainment, impacting overall national development. By focusing on these regions, policymakers can design targeted interventions to uplift educational standards and promote equitable growth.
Implications for National Development
Low literacy rates in these states affect various aspects of national development, including economic growth, health outcomes, and social cohesion. Educated populations are better equipped to contribute to the economy and society, leading to improved living standards and reduced poverty. Therefore, enhancing literacy in these regions is essential for the holistic development of the country.
The Role of Government and Community
Government initiatives alone may not suffice to improve literacy rates. Community involvement and local support are vital for the successful implementation of educational programs. By fostering partnerships between government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and local communities, it is possible to create a more effective and sustainable approach to education.
The Need for Continued Efforts
Despite existing programs, the challenges faced by the least literate states indicate the need for continued and intensified efforts. Evaluating the effectiveness of current initiatives and making necessary adjustments will be key to achieving long-term improvements in literacy rates.
Historical Context
Educational Challenges in India
Historically, India has struggled with educational disparities due to various socio-economic factors. Post-independence, the country has made significant strides in improving literacy rates through numerous educational reforms and policies. However, certain states have lagged behind due to persistent challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, socio-economic issues, and regional disparities.
Key Educational Initiatives
Several key initiatives have been launched to address literacy challenges, including the National Education Policy (NEP) and various state-specific programs. These initiatives aim to provide equitable access to quality education, enhance teacher training, and improve school facilities. Despite these efforts, the progress in some states has been slower, requiring continued focus and innovation.
Key Takeaways from “Three Least Literate States of India”
| Serial Number | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | The three least literate states in India are Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Arunachal Pradesh. |
| 2 | Socio-economic factors, including poverty and lack of infrastructure, significantly impact literacy rates. |
| 3 | Government initiatives such as SSA and Beti Bachao Beti Padhao aim to improve literacy but need more targeted implementation in these states. |
| 4 | Community involvement is crucial for the success of educational programs and reforms. |
| 5 | Continued and intensified efforts are needed to address the root causes of low literacy and promote national development. |
Important FAQs for Students from this News
What are the three least literate states in India?
The three least literate states in India are Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Arunachal Pradesh.
What is the literacy rate in Bihar?
The literacy rate in Bihar is approximately 70%.
What factors contribute to low literacy rates in these states?
Low literacy rates in these states are attributed to socio-economic challenges, including poverty, lack of infrastructure, limited access to quality education, and cultural barriers such as gender inequality.
What government initiatives are aimed at improving literacy rates?
Key government initiatives include the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) and the Beti Bachao Beti Padhao scheme, which focus on enhancing educational infrastructure, promoting gender equality, and increasing enrollment rates.
How can communities contribute to improving literacy rates?
Communities can support literacy improvements by engaging in educational initiatives, supporting local schools, and advocating for better educational resources and policies.
Some Important Current Affairs Links

















