Understanding States and Languages in India
Introduction to States and Languages
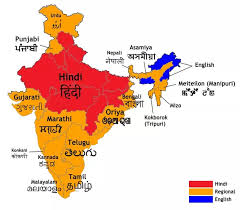
India is a diverse nation with a rich cultural heritage, and its linguistic landscape is a testament to this diversity. The country is home to a plethora of languages, spoken across its 28 states and 8 Union territories. This diversity is not just a cultural feature but also plays a significant role in the administration and functioning of the government. Each state has its own set of languages, and understanding these can provide insights into regional identities and administrative practices.
The Importance of Linguistic Diversity
Linguistic diversity in India is a crucial element of its democratic fabric. The Constitution of India recognizes 22 languages under the Eighth Schedule, highlighting the importance of linguistic representation in governance. These languages are used in various state governments, educational institutions, and media, reflecting the regional character of each state. This linguistic recognition ensures that cultural heritage is preserved and promoted at the regional level, fostering a sense of identity and belonging among the people.
States and Their Official Languages
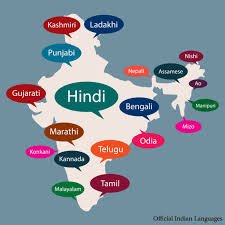
Each state in India has adopted its own official language(s) based on the linguistic composition of its population. For instance, Hindi is widely spoken in the northern states, while states in the south like Tamil Nadu and Karnataka have Tamil and Kannada as their official languages, respectively. In addition to these, states such as Maharashtra and Gujarat have Marathi and Gujarati as their primary languages. This linguistic classification helps in effective administration and ensures that government policies are communicated in a language understood by the majority of the population.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the recognition of multiple languages, India faces challenges related to language policy and implementation. Issues such as language preservation, the need for uniformity in education, and administrative efficiency often arise. However, these challenges also present opportunities for promoting multilingualism and regional development. By addressing these issues, India can enhance its administrative efficiency and ensure that all linguistic communities are adequately represented and served.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between states and languages in India is crucial for anyone preparing for government exams. It not only provides insights into the administrative structure but also helps in appreciating the cultural richness of the country. This knowledge is essential for roles in teaching, policing, banking, railways, defence, and civil services, where an understanding of regional languages and their impact on governance can be a significant advantage.
Why this News is Important
Significance for Governance and Administration
The linguistic diversity of India is not just a cultural trait but a critical element of its governance and administration. Recognizing and understanding the official languages of each state is vital for effective communication between the government and the people. This knowledge ensures that policies are implemented in a manner that respects regional linguistic preferences, thereby fostering better governance and administrative efficiency.
Impact on Education and Employment
The knowledge of state languages is crucial for students preparing for government exams. It impacts various sectors, including education and employment. Understanding the official languages helps in preparing for roles that require communication with the public in regional languages, thus enhancing job readiness and effectiveness in roles such as teaching, police services, and civil administration.
Preservation of Cultural Heritage
Linguistic diversity also plays a significant role in preserving cultural heritage. By recognizing and using regional languages, India ensures that its rich cultural tapestry is maintained and promoted. This is particularly important for students who will be involved in cultural and educational roles, as it helps in understanding and appreciating the diverse cultural background of the country.
Regional Development
Language recognition can drive regional development by addressing local needs and ensuring that governmental initiatives are aligned with regional linguistic capabilities. This alignment can lead to more effective implementation of development programs and policies, contributing to balanced regional growth.
Enhancing Multilingual Skills
For students preparing for various government positions, understanding and acquiring multilingual skills can be beneficial. It prepares them for roles that may require interaction in multiple languages, thus broadening their employment opportunities and enhancing their professional capabilities.
Historical Context: Evolution of Languages in India
Early Linguistic Diversity
India’s linguistic diversity dates back to ancient times, with languages evolving from the Indo-Aryan and Dravidian families. Early texts, such as the Vedas and Upanishads, reflect the rich linguistic heritage of the country. Over the centuries, regional languages developed distinct identities influenced by historical events, migrations, and cultural exchanges.
Colonial Influence and Language Policy
During the British colonial period, language policies were introduced that impacted regional languages and their use in administration. The introduction of English as a medium of instruction in schools and as a language of administration led to significant changes in the linguistic landscape of India.
Post-Independence Language Policy
After gaining independence in 1947, India adopted a multilingual approach to accommodate its diverse linguistic communities. The Constitution of India, adopted in 1950, recognized the need for linguistic representation and included provisions for the use of regional languages in administration. The Eighth Schedule was later added to recognize 22 languages, ensuring their promotion and use in various state governments and institutions.
Current Linguistic Scenario
Today, India’s linguistic policy continues to evolve, balancing the need for linguistic diversity with administrative efficiency. The recognition of multiple languages reflects the country’s commitment to preserving its cultural heritage while addressing the practical needs of governance and administration.
Key Takeaways from “States and Languages in India”
| Serial Number | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | India recognizes 22 languages under the Eighth Schedule. |
| 2 | Each state in India has its own set of official languages. |
| 3 | Linguistic diversity impacts governance and administration. |
| 4 | Language recognition helps in preserving cultural heritage. |
| 5 | Understanding regional languages is crucial for various government roles. |
Important FAQs for Students from this News
1. What is the significance of the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution?
- The Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution recognizes 22 languages and provides them official status. This recognition ensures that these languages are promoted and used in various government functions and educational institutions, reflecting India’s commitment to linguistic diversity and regional representation.
2. How do regional languages impact administrative functions in India?
- Regional languages play a crucial role in administrative functions by facilitating effective communication between the government and the local population. This ensures that policies are implemented in a manner that is understandable and relevant to the people of each state, improving governance and public engagement.
3. Why is understanding state languages important for students preparing for government exams?
- Understanding state languages is important for students preparing for government exams because it helps them in roles that require interaction with the public in regional languages. It also enhances their ability to work effectively in diverse linguistic environments, which is crucial for positions in teaching, policing, and administrative services.
4. How does linguistic diversity contribute to cultural preservation in India?
- Linguistic diversity contributes to cultural preservation by maintaining and promoting regional languages and their associated cultural practices. Recognizing and using these languages helps in preserving the rich cultural heritage of different regions, ensuring that traditional knowledge and practices are passed down through generations.
5. What challenges does India face in managing its linguistic diversity?
- India faces challenges such as ensuring the preservation of lesser-spoken languages, maintaining uniformity in education, and addressing administrative inefficiencies that arise from the use of multiple languages. Balancing these issues requires effective language policies and practices that respect linguistic diversity while promoting efficient governance.
Some Important Current Affairs Links