INS Himgiri inducted into the Indian Navy under Project 17A. Built by GRSE, this indigenous stealth frigate features BrahMos missiles, Barak-8 SAM, and advanced EW systems.
INS Himgiri — India’s Indigenous Stealth Frigate Joins the Indian Navy
Introduction
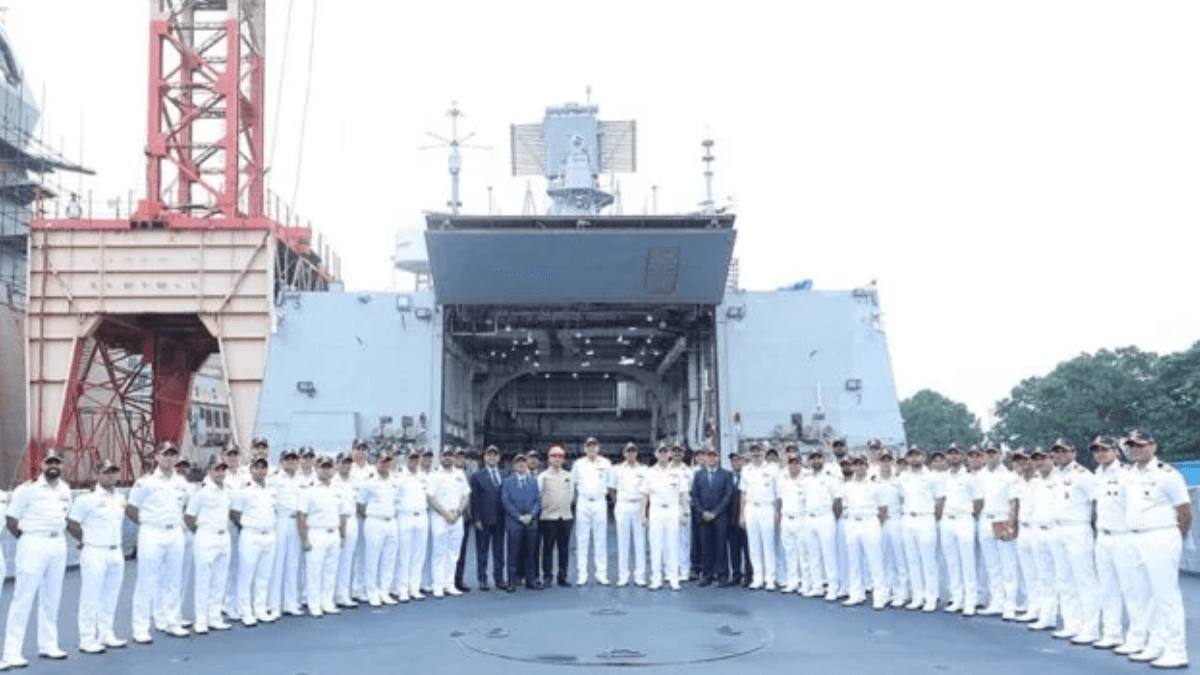
On 31 July 2025, the Indian Navy officially inducted INS Himgiri, a state‑of‑the‑art Nilgiri‑class (Project 17A) stealth guided‑missile frigate, built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE) in Kolkata. This marks a milestone in India’s journey toward defence self‑reliance under the “Aatmanirbhar Bharat” initiative
Legacy Reborn: Reviving INS Himgiri Name
The newly commissioned frigate revives the legacy of the original Leander‑class INS Himgiri, which served the Navy for nearly 30 years before its decommissioning on 6 May 2005. This new vessel, Yard 3022 of the Nilgiri‑class, is the first P‑17A ship constructed by GRSE, underlining expanded fabrication capacity beyond Mumbai’s MDL yard
Cutting‑Edge Design and Construction
Designed by the Warship Design Bureau and managed by the Kolkata-based Warship Overseeing Team, INS Himgiri reflects the Integrated Construction approach—a modular, ergonomic and schedule-driven shipbuilding philosophy that ensures timely delivery and high quality
Technological Features and Armament
The frigate displaces around 6,342–6,670 tonnes, measures approximately 142.5 m in length, achieves top speeds of 30–32 knots, and carries a complement of ~225 personnel Key systems include:
- CODOG propulsion: Combined Diesel or Gas engines driving controllable‑pitch propellers via Integrated Platform Management System (IPMS)
- Combat systems: Integrated Bridge System (IBS), Combat Management System (CMS), Advanced Composite Communication Suite (ACCS), ship‑internal databus
Armaments include:
- Eight vertical‑launch BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles for surface and land attacks
- Barak‑8 LR‑SAM missiles for air defence
- Lightweight Varunastra anti‑submarine torpedoes, 127 mm naval gun, and AK‑630 rapid‑fire CIWS
- Sensors & EW suite: MF‑STAR AESA radar, Shakti EW suite, surface surveillance radar, airborne AEW radar, HUMSA‑NG sonar
Strategic and Industrial Significance
The induction of INS Himgiri signifies India’s strategic push toward achieving a fleet strength of around 170–175 warships by 2035, fully aligned with indigenization goalsWith approximately 75% indigenous content, the project has engaged over 200 MSMEs, generating roughly 4,000 direct and 10,000 indirect jobs—a hallmark of India’s growing defense industrial base
Why This News Is Important
Strategic Defence Boost
The induction of INS Himgiri reinforces India’s blue‑water naval capabilities, enabling the Indian Navy to project power across the Indo‑Pacific region. The vessel significantly enhances operational versatility with modern anti‑air, anti‑surface, and anti‑submarine warfare systems—critical for future maritime dominance.
Atmanirbhar Bharat in Action
Built indigenously with ~75% local content, the frigate showcases India’s ability to design and manufacture sophisticated naval platforms. This self‑manufacturing achievement not only reduces dependency on foreign suppliers but also strengthens national technological resilience.
Shipbuilding and Economic Impact
Himgiri’s construction underscores the rising role of GRSE as a major warship builder, diversifying naval construction beyond MDL. The project’s massive MSME involvement contributes to employment and industrial growth, supporting India’s long-term economic and security objectives.
Historical Context
Evolution of INS Himgiri Name
The original INS Himgiri (Leander-class) served from the 1970s until May 6, 2005, earning distinguished service records. The revival of the name embodies legacy and renewal
Project 17A and Naval Modernisation
P‑17A (Nilgiri‑class) represents the next-generation evolution of the Shivalik class. Conceived in the early 2010s, the series includes seven stealth frigates designed by the Warship Design Bureau, built under a ₹21,833 crore contract. Expected to be fully commissioned between 2024–2027, the program marks a major leap in indigenous stealth and combat warfare capability
Prior Ships
- INS Nilgiri (lead ship) commissioned on 15 January 2025
- INS Udaygiri (second GRSE/MDL-built) delivered on 1 July 2025
Himgiri follows as the third delivery, with further ships like Taragiri, Mahendragiri, Dunagiri, and Vindhyagiri poised for launch through 2026
Key Takeaways from INS Himgiri Induction
| S. No. | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | INS Himgiri inducted on 31 July 2025, built by GRSE under Project 17A. |
| 2 | Stealth frigate with ~75% indigenous content, aligned with ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’. |
| 3 | Main armament includes BrahMos missiles, Barak‑8 SAM, torpedoes, and advanced guns and CIWS. |
| 4 | Advanced systems: CODOG propulsion, IPMS, IBS, CMS, ACCS, MF‑STAR radar, HUMSA‑NG sonar. |
| 5 | Strategic significance: Furthering Indian Navy’s goal of 170–175 warships by 2035; major boost to indigenous shipbuilding. |
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is INS Himgiri?
INS Himgiri is a Nilgiri-class stealth guided missile frigate, built indigenously under Project 17A by Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata.
Q2. When was INS Himgiri inducted into the Indian Navy?
INS Himgiri was formally inducted on 31 July 2025.
Q3. Which major missile system is installed on INS Himgiri?
The ship is equipped with BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles, among other advanced weapon systems.
Q4. What is Project 17A?
Project 17A is an Indian Navy initiative to build seven advanced stealth frigates, evolving from the earlier Shivalik-class warships.
Q5. What is the significance of the INS Himgiri’s name?
It revives the legacy of an earlier INS Himgiri (a Leander-class frigate) that served from the 1970s until its decommissioning in 2005.
Q6. What are the ship’s stealth features?
INS Himgiri uses advanced stealth technology including radar-absorbent materials, low-RCS design, and integrated electronic warfare systems.
Q7. What is the propulsion system used in INS Himgiri?
It operates on a CODOG (Combined Diesel or Gas) propulsion system, offering high-speed mobility and operational flexibility.
Q8. What is the role of GRSE in Indian naval shipbuilding?
GRSE is one of India’s premier shipyards and the first non-MDL unit to construct Project 17A ships, enhancing decentralized defence production.
Q9. How does this news link with Atmanirbhar Bharat?
INS Himgiri has approximately 75% indigenous content, aligning with the government’s goal of defence self-reliance under Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Q10. How many total warships are planned under the Navy’s modernization goals?
The Indian Navy aims to achieve a fleet of 170–175 warships by 2035, with a strong emphasis on indigenous design and manufacturing.
Some Important Current Affairs Links