Hydrogen powered train in Haryana marks India’s first step towards eco-friendly rail transport. Learn about the project, route, technology, exam relevance, key facts, and government initiatives in this detailed current affairs article.
India’s First Hydrogen-Powered Train to Launch in Haryana: A New Milestone in Green Mobility
The Government of India and Indian Railways are set to introduce the country’s first hydrogen-powered train in Haryana, marking a transformational shift in Indian rail transport towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. The pilot project, planned to run on the Jind–Sonipat railway route, is now in its final commissioning phase and is expected to officially launch soon.
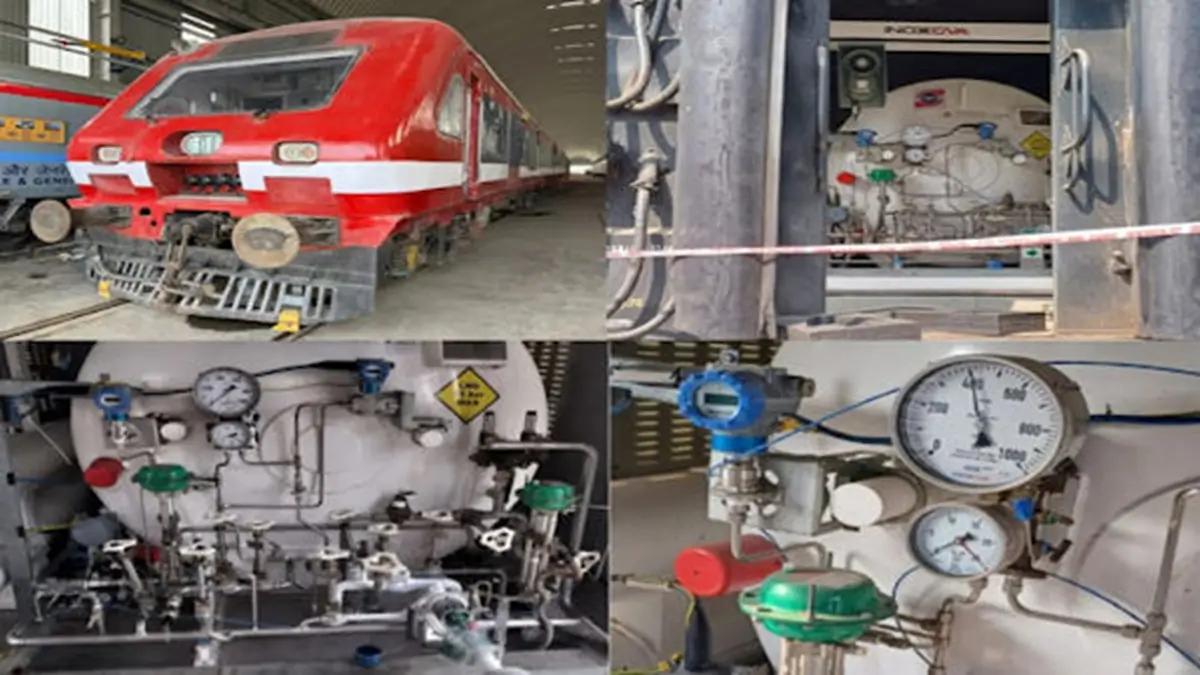
Unlike conventional diesel locomotives, this train will be powered by green hydrogen — produced via electrolysis and stored at a dedicated hydrogen plant established in Jind, Haryana. With a 3,000 kg hydrogen storage facility already set up, the system is designed to ensure smooth and uninterrupted operations.
The initiative is part of Indian Railways’ broader efforts to decarbonize rail transport and reduce dependency on fossil fuels. Hydrogen fuel cells on the train produce electricity through a chemical process combining hydrogen and oxygen, emitting only water vapor — making this one of the cleanest forms of transport available today.
Technological advancements in the train include zero-emission operation, improved energy efficiency, and modern passenger amenities. The project is also being monitored closely by authorities to ensure safety and reliability, with specifications laid out by the Research Designs and Standards Organization (RDSO).
The pilot will serve as a model for future hydrogen train deployments across other non-electrified routes in India. This aligns with India’s climate commitments and net-zero targets, supporting the nation’s transition to renewable and clean energy usage in transportation.
Why This News Is Important for Exam Aspirants
A Breakthrough in India’s Clean Transport Strategy
This news is significant for students preparing for government exams such as UPSC Civil Services (IAS/IPS), SSC, Railways, Banking, and State PSCs because it reflects a major policy priority of the Indian government — sustainable and clean energy adoption. The hydrogen train initiative shows India’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions and achieving its climate goals while promoting innovation in public infrastructure.
Relevance Across Multiple Syllabus Topics
For UPSC and State PSC exams, this development ties directly to current affairs topics including:
- Environment and Ecology (Clean Energy Transitions)
- Science and Technology Applications
- Infrastructure & Transport Development
- Government Initiatives and Policies
Understanding the mechanics and implications of hydrogen fuel cell technology will help candidates answer questions related to renewable energy and green mobility.
Policy Implementation and National Goals
For aspirants in Railways, Banking, and Defence exams, this news highlights how policy frameworks translate into high-impact projects. It exemplifies inter-agency coordination, including strategic planning by Railway authorities, state governments, and technical bodies like RDSO.
Overall, the hydrogen train project is a cross-cutting topic that blends technology, environment, and governance, making it crucial for both objective answers and essay writing in competitive examinations.
Historical Context: India’s Journey Towards Hydrogen Rail Technology
While India has long relied on electric and diesel trains, the shift to hydrogen propulsion represents an important technological evolution in rail transport. Globally, several countries — including Germany, France, Sweden, and China — have already experimented with hydrogen trains to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Indian Railways’ first green hydrogen project began under the “Hydrogen for Heritage” initiative, aimed initially at heritage and non-electrified routes. This plan involves retrofitting existing diesel multiple units (DMUs) with hydrogen fuel cell technology.
The Integral Coach Factory (ICF) in Chennai has played a key role in manufacturing the hydrogen train coaches. In parallel, hydrogen production and refueling infrastructure are being developed in Haryana to support daily operations, a critical element for scalable deployment of hydrogen propulsion in India.
This move aligns with India’s broader energy strategy, including commitments under the Paris Climate Agreement and net-zero emission goals by 2070. It signals a future where rail transport not only connects people but also embodies green innovation.
Key Takeaways from “India’s First Hydrogen-Powered Train Launch”
| S.No. | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | India’s first hydrogen-powered train will be launched in Haryana on the Jind–Sonipat route as a pilot project. |
| 2 | The train uses green hydrogen fuel cells, producing zero carbon emissions during operation. |
| 3 | A hydrogen plant with 3,000 kg storage capacity has been set up at Jind to support refueling. |
| 4 | The project aligns with India’s aim to reduce fossil fuel dependence and support sustainable mobility. |
| 5 | It demonstrates advanced technological adoption by Indian Railways and sets a precedent for future eco-friendly train projects. |
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions (For Government Exam Preparation)
1. Which state will launch India’s first hydrogen-powered train?
Haryana will launch India’s first hydrogen-powered train on the Jind–Sonipat route.
2. What is hydrogen fuel cell technology?
It is a technology that generates electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen, producing water vapor as the only by-product, making it a zero-emission energy source.
3. Why is hydrogen considered a clean fuel?
Because it does not release carbon dioxide during energy generation and helps reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
4. Which organization sets safety and technical standards for railway projects in India?
The Research Designs and Standards Organization (RDSO) under the Ministry of Railways.
5. What is green hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power through the process of electrolysis.
6. Under which broader mission does this project align?
It aligns with India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission and Net Zero 2070 targets.
7. Why is this project important for Indian Railways?
It reduces dependence on diesel, lowers fuel costs in the long term, and supports sustainable transport.
8. Which manufacturing unit developed the hydrogen-powered coaches?
The Integral Coach Factory (ICF), Chennai.
9. On which type of routes will hydrogen trains be most useful?
On non-electrified and remote railway routes.
10. Which exams commonly ask questions from such topics?
UPSC (IAS/IPS), State PSCs, SSC, Railways (RRB), Banking exams, and Defence recruitment exams.
Some Important Current Affairs Links