The Top 10 Strongest Metals in the World: A Comprehensive Guide
Metals have been a cornerstone of human civilization, enabling advancements in technology, infrastructure, and industry. Understanding the strength of metals is crucial for various applications, from constructing buildings and bridges to manufacturing automobiles and aircraft. This article explores the top 10 strongest metals in the world, detailing their properties, uses, and significance.
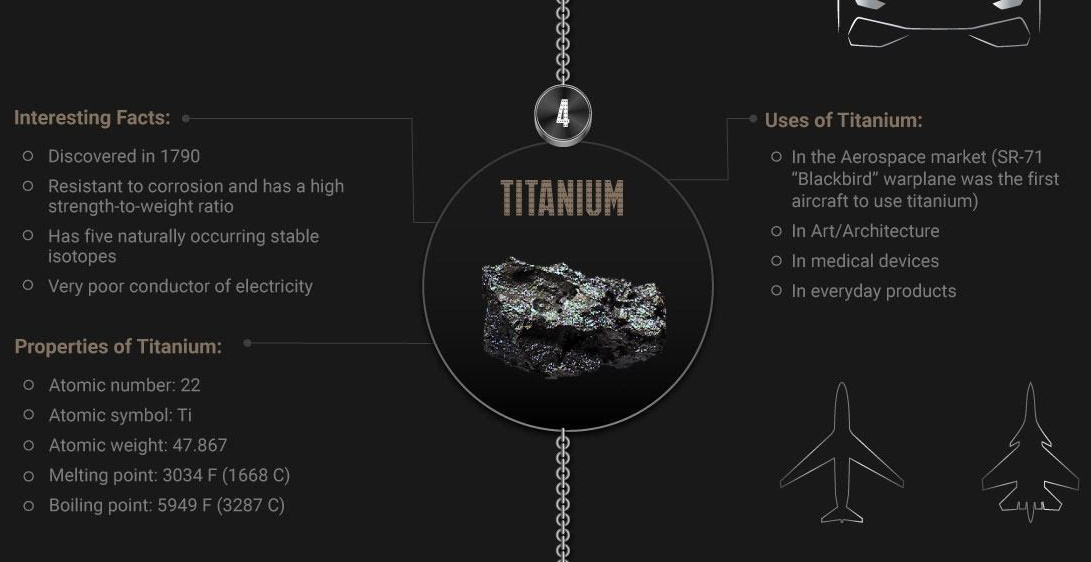
Titanium: The Powerhouse of Strength and Lightness
Titanium is renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications. It is as strong as steel but 45% lighter, and it exhibits excellent corrosion resistance.
Tungsten: The Ultimate in High Temperature Endurance
Tungsten boasts the highest melting point of all metals (3422°C). Its incredible hardness and density make it essential in applications requiring durability under extreme conditions, such as in electrical contacts and cutting tools.
Chromium: The Shiny Armor
Chromium is known for its shiny finish and corrosion resistance. It is a key component in stainless steel, providing hardness and a lustrous finish that is both aesthetically pleasing and protective.
Steel: The Backbone of Modern Industry
Steel is an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon. Its various grades, such as carbon steel and stainless steel, offer a balance of strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear and corrosion, making it indispensable in construction and manufacturing.
Inconel: The Super Alloy
Inconel, a family of nickel-chromium-based superalloys, exhibits exceptional resistance to oxidation and corrosion at high temperatures. It is widely used in the aerospace industry, particularly in jet engines and gas turbines.
Osmium: The Dense and Durable Metal
Osmium is one of the densest elements and is known for its extreme hardness and high melting point. These properties make it valuable in applications requiring durability and resistance to wear, such as in fountain pen nibs and electrical contacts.
Iridium: The Resilient Metal
Iridium, another dense metal, is highly resistant to corrosion and high temperatures. It is often used in spark plugs, crucibles for high-temperature experiments, and deep-sea telecommunication cables.
Vanadium: The Flexible Enhancer
Vanadium is a vital alloying element that increases the strength, toughness, and heat resistance of steel. It is extensively used in automotive parts, tools, and aerospace components.
Zirconium: The Resistant Element
Zirconium is notable for its corrosion resistance, especially in aggressive environments. It is commonly used in nuclear reactors due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and radiation without degrading.
Lithium: The Lightweight Power Source
Lithium is the lightest metal and is crucial in the production of batteries, especially lithium-ion batteries that power a wide range of electronic devices and electric vehicles.
Conclusion
The strength and properties of these metals make them indispensable across various industries. Understanding their characteristics helps in choosing the right material for specific applications, ensuring safety, efficiency, and longevity.

Why This News Is Important
Relevance to Exam Aspirants
Knowledge of the strongest metals and their properties is crucial for aspirants preparing for exams in fields like engineering, defense, and civil services. Questions related to material science and industrial applications often feature in competitive exams.
Industrial and Technological Significance
These metals play a significant role in advancing technology and industry. Understanding their applications can help candidates appreciate their importance in everyday technology and infrastructure, enriching their general knowledge.
Practical Applications and Innovations
Learning about these metals highlights their practical applications and the innovations they enable. This knowledge can inspire future engineers and technologists to contribute to advancements in materials science.
Historical Context
Evolution of Metal Use
The use of metals dates back to ancient civilizations, where they were primarily used for tools and weapons. The discovery and use of stronger metals have historically driven technological progress, from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age, and now to the modern era dominated by advanced alloys.
Impact on Industrial Revolution
The development and refinement of steel played a pivotal role in the Industrial Revolution, enabling the construction of railways, buildings, and machinery that fueled economic growth and societal development.
Modern Advancements
In recent times, the discovery and utilization of superalloys and advanced materials like titanium and Inconel have revolutionized industries such as aerospace, medical implants, and electronics, showcasing the continuous evolution of material science.
Key Takeaways from “The Top 10 Strongest Metals in the World”
| S.No | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | Titanium offers high strength and low weight, crucial for aerospace and medical applications. |
| 2 | Tungsten has the highest melting point and is essential in extreme temperature conditions. |
| 3 | Chromium’s corrosion resistance makes it vital for stainless steel production. |
| 4 | Steel’s versatility and various grades make it the backbone of modern industry. |
| 5 | Inconel’s resistance to oxidation and high temperatures makes it indispensable in aerospace. |
Important FAQs for Students from this News
Q1: What are the factors considered while ranking the strength of metals?
A: The strength of metals is determined by various factors including hardness, tensile strength, density, and resistance to corrosion and high temperatures.
Q2: How are these strongest metals utilized in everyday life?
A: These metals are utilized in various industries such as aerospace, construction, electronics, and healthcare for applications ranging from structural components to electronic devices and medical implants.
Q3: Can you provide examples of how these metals contribute to technological advancements?
A: Titanium, for instance, is used in aircraft frames, artificial joints, and sporting equipment due to its strength and lightweight properties, while tungsten is crucial for high-temperature applications like light bulb filaments and rocket nozzles.
Q4: What are some historical milestones in the development of metals?
A: Historical milestones include the discovery of bronze and iron, the Industrial Revolution driven by advancements in steel production, and modern innovations in superalloys for aerospace and defense applications.
Q5: How do these metals impact environmental sustainabi lity?
A: While metals like lithium are essential for renewable energy storage solutions, the extraction and processing of metals can have environmental implications. Efforts are being made to improve recycling and sustainability practices in the metal industry.
Some Important Current Affairs Links