Uganda Launches Groundbreaking Ebola Vaccine Trial: A Step Towards Global Health Security
Introduction to the Ebola Vaccine Trial
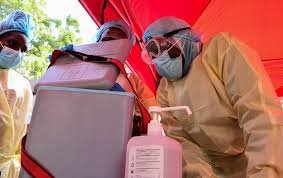
Uganda has recently launched a groundbreaking clinical trial for a new Ebola vaccine, marking a significant milestone in the fight against the deadly virus. The trial, which is being conducted in collaboration with international health organizations, aims to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the vaccine in preventing Ebola infections. This initiative comes at a critical time, as the world continues to grapple with emerging infectious diseases and the need for effective vaccines.
The Need for a New Ebola Vaccine
Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a severe and often fatal illness that has caused numerous outbreaks in Africa over the past few decades. While vaccines like rVSV-ZEBOV have been effective against the Zaire strain of Ebola, there is a pressing need for vaccines that can combat other strains, such as the Sudan virus, which has no approved vaccine yet. The new trial in Uganda focuses on developing a vaccine that can provide broad-spectrum protection against multiple Ebola strains.
Collaborative Efforts in Vaccine Development
The trial is a result of a collaborative effort between Uganda’s Ministry of Health, the World Health Organization (WHO), and several international research institutions. This partnership highlights the importance of global cooperation in addressing public health challenges. The vaccine candidate being tested has shown promise in preclinical studies, and the trial aims to confirm its effectiveness in human subjects.
Impact on Global Health Security
The successful development of a new Ebola vaccine would not only benefit Uganda but also enhance global health security. It would provide a critical tool for preventing future outbreaks and reducing the mortality rate associated with the disease. Additionally, the trial underscores the importance of investing in research and development to combat emerging infectious diseases.
Why This News is Important
Addressing a Critical Public Health Challenge
The launch of the Ebola vaccine trial in Uganda is a significant development in the fight against one of the world’s deadliest diseases. Ebola outbreaks have caused widespread devastation in Africa, and the lack of a vaccine for certain strains has been a major concern. This trial represents a proactive step towards addressing this gap.
Strengthening Global Health Infrastructure
The trial highlights the importance of international collaboration in tackling global health challenges. By working together, countries and organizations can pool resources and expertise to develop effective solutions. This initiative also strengthens Uganda’s health infrastructure and positions it as a leader in medical research.
Preparing for Future Outbreaks
The development of a new Ebola vaccine is crucial for preparing for future outbreaks. It not only provides a preventive measure but also enhances the global capacity to respond to emerging infectious diseases. This is particularly important in the context of climate change and increasing human-animal interactions, which are contributing to the rise of zoonotic diseases.
Historical Context
Ebola Virus: A Persistent Threat
The Ebola virus was first identified in 1976 during simultaneous outbreaks in Sudan and the Democratic Republic of Congo. Since then, there have been multiple outbreaks, with the most devastating occurring in West Africa between 2014 and 2016, claiming over 11,000 lives. The virus is transmitted through direct contact with bodily fluids and has a high mortality rate.
Previous Vaccine Efforts
The rVSV-ZEBOV vaccine, developed during the 2014-2016 outbreak, has been effective against the Zaire strain of Ebola. However, other strains, such as the Sudan virus, remain a challenge. The current trial in Uganda builds on previous research and aims to address this gap by developing a vaccine that can target multiple strains.
Uganda’s Role in Ebola Research
Uganda has been at the forefront of Ebola research and response efforts. The country has experienced several outbreaks in the past and has developed a robust system for disease surveillance and containment. This trial is a testament to Uganda’s commitment to advancing global health.
Key Takeaways from This News
| S.No. | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | Uganda has launched a groundbreaking clinical trial for a new Ebola vaccine. |
| 2 | The trial focuses on developing a vaccine effective against multiple Ebola strains. |
| 3 | It is a collaborative effort involving Uganda’s Ministry of Health, WHO, and international research institutions. |
| 4 | The successful development of the vaccine would enhance global health security. |
| 5 | The trial underscores the importance of international cooperation in addressing public health challenges. |
Important FAQs for Students from this News
- What is the purpose of the Ebola vaccine trial in Uganda?
The trial aims to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a new Ebola vaccine, particularly against the Sudan virus strain, which currently has no approved vaccine. - Which organizations are involved in the Ebola vaccine trial?
The trial is a collaborative effort between Uganda’s Ministry of Health, the World Health Organization (WHO), and several international research institutions. - Why is the Sudan virus strain significant?
The Sudan virus is one of the strains of the Ebola virus, and unlike the Zaire strain, there is no approved vaccine for it. This trial seeks to address this gap. - How does this trial contribute to global health security?
A successful vaccine would provide a critical tool for preventing future Ebola outbreaks, reducing mortality rates, and enhancing global preparedness for infectious diseases. - What is the historical significance of Uganda in Ebola research?
Uganda has experienced multiple Ebola outbreaks and has developed a robust disease surveillance and containment system, making it a key player in Ebola research. - What are zoonotic diseases, and why are they relevant to this news?
Zoonotic diseases are infections transmitted from animals to humans. Ebola is a zoonotic disease, and its rise is linked to increased human-animal interactions and climate change.
Some Important Current Affairs Links