India Welcomes Egypt, Iran, UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Ethiopia Joining BRICS
BRICS Expansion: A New Chapter
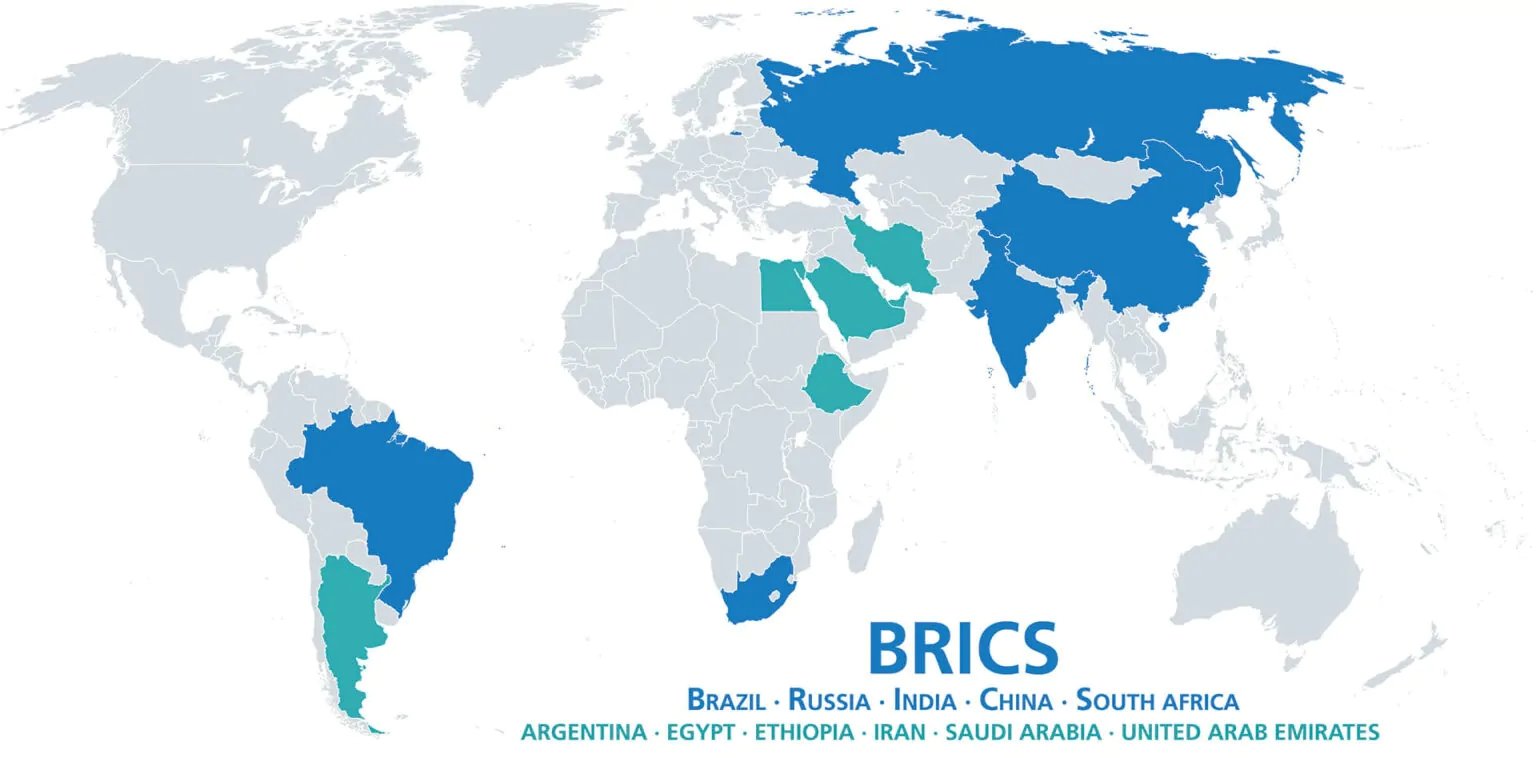
In a significant move, BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) has expanded its membership to include Egypt, Iran, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Saudi Arabia, and Ethiopia. This decision was announced during the 15th BRICS Summit held in Johannesburg, South Africa. The inclusion of these nations is seen as a strategic enhancement of the group’s global influence and economic cooperation.
Strategic Implications for India
India, a founding member of BRICS, has warmly welcomed the inclusion of the new members. This expansion is expected to bolster economic ties and enhance geopolitical cooperation. For India, the entry of these nations into BRICS offers opportunities for increased trade, investment, and collaboration in various sectors such as energy, technology, and infrastructure.
Economic Benefits and Trade Opportunities
The addition of resource-rich nations like Saudi Arabia and the UAE is particularly significant for India’s energy security. With Iran, a key oil supplier, joining the bloc, India can look forward to more stable and possibly more favorable energy deals. Additionally, Ethiopia’s inclusion highlights the potential for agricultural cooperation, given its significant agricultural sector.
Enhancing Geopolitical Influence
The expanded BRICS now encompasses more than just emerging economies but also pivotal players in the Middle East and Africa. This diverse representation enhances the group’s ability to address global challenges and increases its bargaining power in international forums. For India, this means a stronger platform to advocate for reforms in global governance structures, including the United Nations and financial institutions like the IMF and World Bank.
Potential Challenges and Diplomatic Dynamics
While the expansion presents numerous opportunities, it also brings challenges. The differing political landscapes and economic priorities of the new members may require adept diplomacy and negotiation skills. India, with its experience in multilateral diplomacy, is well-positioned to navigate these complexities and leverage the expanded BRICS framework to its advantage.
Why this News is Important
Enhancing India’s Economic and Energy Security
The inclusion of Egypt, Iran, UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Ethiopia into BRICS holds significant importance for India. It opens new avenues for economic cooperation and enhances energy security. With major oil suppliers like Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Iran now part of BRICS, India can look forward to more stable and possibly more favorable energy deals, which is crucial for its growing economy.
Strengthening Geopolitical Stature
For India, the expanded BRICS means a stronger collective voice in international affairs. The inclusion of countries from the Middle East and Africa diversifies the group’s representation, making it a more influential body in global governance. This can help India in advocating for reforms in global institutions like the UN, IMF, and World Bank, aligning with its long-term strategic interests.
Opportunities for Trade and Investment
The new BRICS members bring with them vast economic potentials. Countries like Ethiopia offer new markets for Indian goods and opportunities for investment in agriculture and infrastructure. Enhanced trade relations with these nations can contribute significantly to India’s economic growth and job creation.
Diplomatic and Strategic Challenges
The expansion of BRICS also brings challenges. The diverse political and economic backgrounds of the new members will require India to navigate complex diplomatic terrains. However, India’s experience in multilateral diplomacy equips it to manage these dynamics effectively, turning potential challenges into opportunities for deeper cooperation.
Aligning with Global Trends
The BRICS expansion reflects broader trends in global geopolitics, where emerging economies are seeking greater influence. India’s active participation and support for this expansion align with its vision of a multipolar world order, where power is more evenly distributed, and emerging economies play a pivotal role.
Historical Context
Origin and Evolution of BRICS
BRICS was originally formed in 2009 as a group of emerging economies—Brazil, Russia, India, and China. South Africa joined in 2010, expanding the group to BRICS. The group’s primary aim was to enhance cooperation among these major emerging economies and to provide a counterbalance to Western-dominated international financial institutions.
Previous Expansions and Partnerships
While the inclusion of South Africa was the first expansion, BRICS has continually sought to expand its influence through partnerships with other emerging economies. The decision to include Egypt, Iran, UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Ethiopia is the most significant expansion since South Africa’s inclusion, reflecting the group’s growing ambitions.
India’s Role in BRICS
India has been a proactive member of BRICS, advocating for stronger economic ties and cooperation in areas like technology, health, and sustainable development. Over the years, India has hosted BRICS summits and initiated various collaborative projects, emphasizing its commitment to the group’s objectives.
BRICS in Global Governance
BRICS has played a crucial role in advocating for reforms in global governance structures. The group has consistently called for greater representation of emerging economies in international institutions like the United Nations, the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Bank. This latest expansion is a step towards strengthening its collective voice in these forums.
Impact of BRICS on Global Economy
The collective economic weight of BRICS has grown significantly over the years. With the inclusion of new members, BRICS now represents a substantial portion of the world’s population and GDP. This enhances its ability to influence global economic policies and trade agreements, positioning it as a formidable bloc in the international arena.
Key Takeaways from BRICS Expansion
| Serial Number | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | BRICS has expanded to include Egypt, Iran, UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Ethiopia. |
| 2 | This expansion enhances India’s economic ties and energy security. |
| 3 | The inclusion of Middle Eastern and African countries strengthens BRICS’ geopolitical influence. |
| 4 | India’s diplomatic skills will be crucial in navigating the diverse priorities of the new members. |
| 5 | The expansion aligns with global trends towards a multipolar world order, increasing the influence of emerging economies. |
Important FAQs for Students from this News
What is BRICS?
BRICS is an acronym for a group of five major emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. The group was formed to enhance economic cooperation and political dialogue among these countries.
Which countries have recently joined BRICS?
The countries that have recently joined BRICS are Egypt, Iran, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Saudi Arabia, and Ethiopia.
Why is the expansion of BRICS significant?
The expansion is significant because it enhances the group’s global influence, economic cooperation, and geopolitical leverage. It includes resource-rich countries that can provide stability and new opportunities for trade and investment.
How does India benefit from the expansion of BRICS?
India benefits through enhanced economic ties, energy security, and a stronger platform to advocate for reforms in global governance. The inclusion of major oil suppliers and new markets can positively impact India’s economy.
What are the challenges associated with the expansion of BRICS?
The challenges include managing the diverse political and economic backgrounds of the new members. India will need to navigate complex diplomatic dynamics to ensure effective cooperation within the expanded group.
Some Important Current Affairs Links