What is the Color of the Sun? Understanding the Science Behind It
Introduction
The Sun, the central star of our solar system, appears yellow to the human eye when viewed from Earth. However, its actual color is a subject of scientific discussion. While many believe it to be yellow or orange, scientific research suggests that the Sun emits white light composed of multiple wavelengths. The perception of its color changes due to atmospheric interference and human vision.
The Science Behind the Sun’s Color
The Sun emits electromagnetic radiation across a spectrum, including visible light, ultraviolet, and infrared. The visible spectrum consists of multiple colors—red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet—which, when combined, produce white light. When seen from space, the Sun appears white because there is no atmospheric interference to scatter the light.
Why Does the Sun Look Yellow from Earth?
On Earth, the atmosphere plays a crucial role in how we perceive the Sun’s color. As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, shorter wavelengths (blue and violet) scatter more than longer wavelengths (yellow, orange, and red). This scattering effect, known as Rayleigh scattering, results in the Sun appearing yellow to the naked eye.
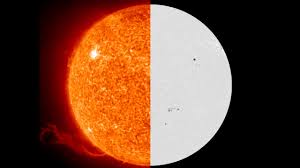
Color of the Sun in Space vs. Earth
Astronauts in space and images captured by satellites show the Sun as white rather than yellow. This is because space lacks an atmosphere to scatter the light, allowing all wavelengths to reach the observer’s eyes equally. The yellowish tint we see on Earth is, therefore, an atmospheric illusion.
Impact of Sunlight on Earth’s Sky Color
The same scattering process that makes the Sun look yellow is responsible for the blue sky. During sunrise and sunset, the Sun appears red or orange because its light must pass through a larger section of the atmosphere, scattering blue and green wavelengths and leaving behind red and orange hues.
Why This News is Important?
Relevance in Science and Astronomy
Understanding the Sun’s true color helps in comprehending the fundamental principles of light and atmospheric interactions. This knowledge is crucial for students preparing for government exams, especially in science and astronomy-related sections.
Impact on Space Research and Observations
Knowing how the Sun’s color appears differently in space and on Earth helps astronomers design better telescopes and instruments for space exploration. It also enhances our understanding of other stars and celestial bodies.
Educational Value for Competitive Exams
Topics related to optics, the scattering of light, and the Sun’s properties are commonly asked in competitive exams, including UPSC, SSC, and railway exams. Understanding the scientific explanation behind the Sun’s color can help candidates answer related questions accurately.
Historical Context
The Evolution of Our Understanding of the Sun’s Color
Historically, ancient civilizations perceived the Sun as a glowing disk of fire, often associating it with deities. With the advancement of optics and scientific observations, researchers discovered that the Sun emits multiple wavelengths of light, ultimately concluding that its true color is white.
Rayleigh Scattering and Optical Discoveries
Lord Rayleigh’s work in the 19th century on the scattering of light provided scientific evidence for why the Sun appears yellow from Earth. This discovery contributed significantly to the field of atmospheric physics.
Space Exploration and the Sun’s True Color
With the advent of space missions and satellite technology, scientists could observe the Sun from outside Earth’s atmosphere. These observations confirmed that the Sun’s light is white, a fact now well-documented by space agencies like NASA.
Key Takeaways from ‘What is the Color of the Sun?’
| S.No. | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1. | The Sun emits white light, composed of multiple wavelengths. |
| 2. | The atmosphere scatters blue and violet wavelengths, making the Sun appear yellow from Earth. |
| 3. | In space, without atmospheric interference, the Sun appears white. |
| 4. | Rayleigh scattering is responsible for the Sun’s color changes and the blue sky. |
| 5. | Understanding the Sun’s color is important for scientific research and competitive exams. |
Important FAQs for Students from this News
1. What is the actual color of the Sun?
The Sun’s actual color is white, as it emits all wavelengths of visible light, which combine to form white light.
2. Why does the Sun appear yellow from Earth?
Due to Rayleigh scattering, shorter wavelengths (blue and violet) scatter more in Earth’s atmosphere, making the Sun appear yellow to our eyes.
3. How does the Sun appear in space?
In space, where there is no atmospheric interference, the Sun appears white instead of yellow.
4. What is Rayleigh scattering?
Rayleigh scattering is a phenomenon where shorter wavelengths of light scatter more than longer wavelengths when passing through the atmosphere, affecting the color perception of objects like the Sun.
5. Why does the Sun appear red during sunrise and sunset?
At sunrise and sunset, the Sun’s light has to travel through a larger portion of the atmosphere, scattering blue and green light and leaving behind red and orange hues.
Some Important Current Affairs Links

















