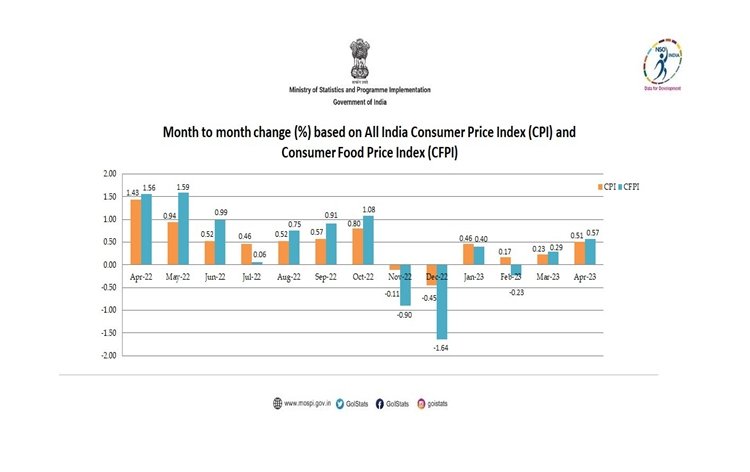
Retail Inflation Drops :18-Month Low of 4.70% in April
In a positive development for the economy, retail inflation in India witnessed a significant decline, reaching an 18-month low of 4.70% in April. This drop in inflation has brought much-needed relief to policymakers, consumers, and businesses across the country. The decline can be attributed to various factors, including reduced food prices and improved supply chain management. This article delves into the reasons behind the decrease in retail inflation and its implications for various sectors.
Why this News is Important:
Positive Impact on Consumers:
The decrease in retail inflation brings good news for consumers. With lower inflation rates, the cost of essential goods and services becomes more affordable, providing relief to the common man. This decline can enhance the purchasing power of individuals and contribute to increased consumer spending, which in turn stimulates economic growth.
Boost to Government’s Efforts:
The government’s continuous efforts to control inflation have yielded positive results. The decline in retail inflation showcases the effectiveness of various measures taken by policymakers to stabilize prices. This achievement strengthens the government’s commitment to ensuring economic stability and improving the overall well-being of citizens.
Historical Context:
To understand the significance of the recent decline in retail inflation, it is important to consider the historical context. Over the years, India has faced several challenges related to inflation, impacting the economy and the livelihoods of its citizens. Inflation rates have fluctuated, with periods of high inflation posing significant obstacles to economic growth and stability.
In recent years, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has implemented various monetary policy measures to curb inflation. These measures include adjusting interest rates, managing liquidity in the banking system, and implementing regulatory policies to control price levels. The current decline in retail inflation can be seen as a positive outcome of these efforts.
Key Takeaways from “Retail Inflation Drops to 18-Month Low of 4.70% in April”:
| Serial Number | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | Retail inflation in India dropped to 4.70% in April, an 18-month low. |
| 2 | Factors contributing to the decrease include reduced food prices and improved supply chain management. |
| 3 | The decline in inflation positively impacts consumers by making essential goods and services more affordable. |
| 4 | The decrease in retail inflation reflects the effectiveness of the government’s measures to control prices. |
| 5 | Over the years, India has faced challenges related to inflation, and the recent decline is a positive development in achieving economic stability. |
Important FAQs for Students from this News
Q: What is retail inflation?
A: Retail inflation refers to the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, leading to a decrease in the purchasing power of money. It is also known as consumer price inflation (CPI) and measures changes in the cost of living for consumers.
Q: How is retail inflation measured in India?
A: In India, retail inflation is primarily measured using the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The CPI tracks the price changes of a basket of goods and services commonly consumed by urban and rural households.
Q: What factors contributed to the decline in retail inflation in April?
A: The decline in retail inflation can be attributed to several factors, including reduced food prices and improved supply chain management. Stable or lower prices of essential commodities play a significant role in moderating inflation rates.
Q: How does the decrease in retail inflation impact the economy?
A: A decrease in retail inflation can have positive effects on the economy. It improves the purchasing power of consumers, stimulates consumer spending, and provides a conducive environment for business growth. Lower inflation rates also contribute to a more stable and predictable economic environment.
Q: What are the implications of the decline in retail inflation for policymakers?
A: The decline in retail inflation provides policymakers with more flexibility in implementing monetary and fiscal policies. It allows them to focus on other areas of economic development, such as investment promotion, employment generation, and infrastructure development.
Some Important Current Affairs Links