Philippine Eagle critically endangered species details, habitat, conservation status, and key facts for UPSC, PSC, Banking, Railway and Defence exams preparation.
Meet One of the Largest Raptors on Earth: The Philippine Eagle
Introduction to the Philippine Eagle
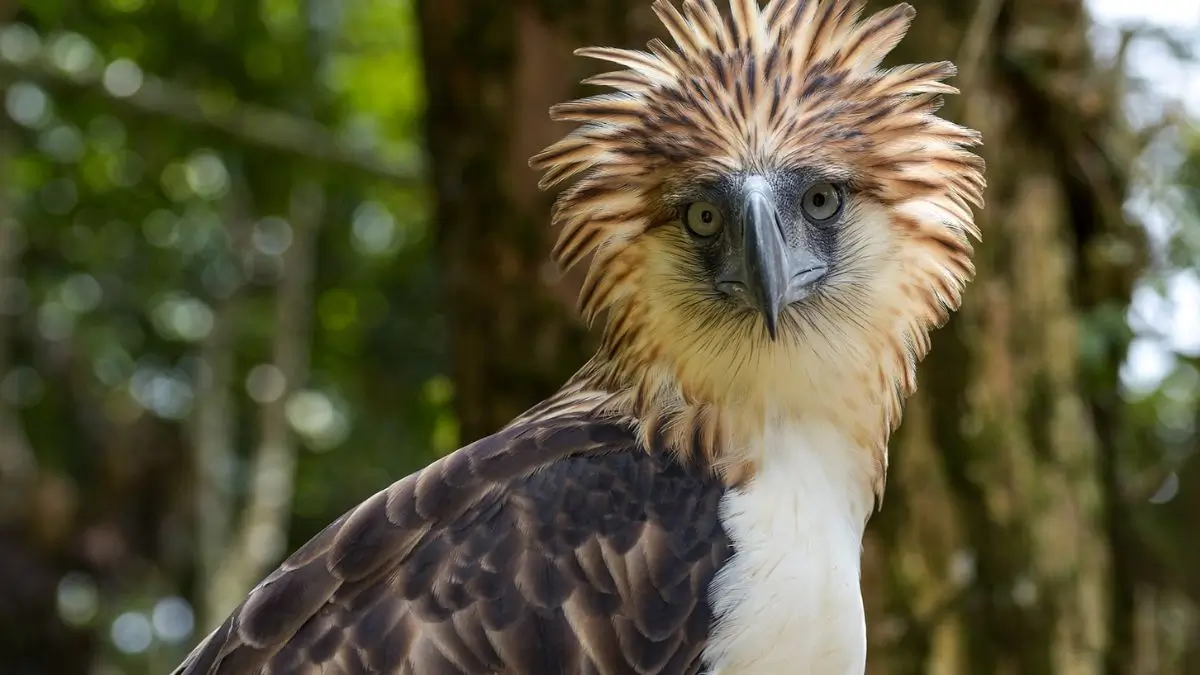
The Philippine Eagle (Pithecophaga jefferyi), also known as the Monkey-Eating Eagle or Great Philippine Eagle, is one of the largest and most powerful birds of prey in the world. It is the national bird of the Philippines, revered for its strength, majestic appearance, and critical ecological role in forest ecosystems. With a body length that can exceed 1 meter and a wingspan nearing 2 meters, this eagle stands among the tallest raptors alive today.
Physical Characteristics and Hunting Adaptations
What truly sets the Philippine Eagle apart is its unique physical structure adapted for life in dense forests. Its sharp hooked beak and strong talons allow it to seize prey with ease, while its broad wings and long tail enable agile flight through thick rainforest canopies. Females are typically larger than males, weighing up to 8 kilograms, and both sexes display an impressive stature that makes them apex predators.
Habitat and Geographic Distribution
This raptor is endemic to the Philippines and restricted to primary forests on the islands of Luzon, Mindanao, Samar, and Leyte. These birds rely on vast tracts of undisturbed dipterocarp forests, and each breeding pair may need territory covering over 100 square kilometres to successfully thrive and raise young.
Conservation Status and Threat Factors
The Philippine Eagle is listed as Critically Endangered by the IUCN, with fewer than 500 mature individuals remaining in the wild. Its population continues to decline due to deforestation, habitat loss, hunting, and human disturbances. The species also suffers from a slow breeding cycle, laying only one egg every two years, which significantly hampers population recovery.
Conservation Efforts and Protection
Several conservation programmes, including habitat protection, anti-poaching enforcement, reintroduction initiatives, and captive breeding efforts, have been introduced to save this iconic bird. Despite these efforts, the future of the Philippine Eagle remains deeply tied to the preservation of the Philippines’ remaining primary rainforests.
Why This News Is Important for Exam Preparations
Environmental and Biodiversity Significance
The Philippine Eagle’s critical status highlights the urgent global challenge of wildlife conservation and the need to protect biodiversity. For government exam subjects like Environment, Ecology, Geography, and Biodiversity, this news is highly relevant. It illustrates the effects of habitat degradation, a major topic in Environment and Ecology syllabus for UPSC, PSCs, and other competitive exams.
Link to Conservation Policies and Legal Frameworks
Understanding the plight of the Philippine Eagle also helps students connect to wildlife protection laws, IUCN Red List classifications, and government/NGO conservation strategies — key components in sections such as Polity, Governance, and International Agreements. The topic lends insights into how endangered species are protected under international conservation frameworks and national wildlife acts.
Integration into Current Affairs Sections
This news topic is pertinent to the Current Affairs section, especially under Environment, Ecology, and Conservation. It teaches students about ongoing global environmental issues, the role of apex predators in ecosystems, and the implications of human activities on endangered wildlife — all of which are frequent themes in government examinations.
Historical Context: Background of the Philippine Eagle
Discovery and Taxonomy
The Philippine Eagle was first observed in the late 19th century and scientifically described in 1896. Known scientifically as Pithecophaga jefferyi, it belongs to the family Accipitridae and is endemic to the Philippines. Its distinctive shaggy crest and impressive size have made it a symbol of the country’s natural heritage.
Cultural and National Importance
Locally known as Haribon — meaning King Bird — the Philippine Eagle is a national symbol of strength and freedom. Efforts to protect it began in earnest as its habitat came under increasing threat from human activities. Through the 20th and 21st centuries, conservation organisations like the Philippine Eagle Foundation have pioneered breeding, research, and habitat restoration efforts to sustain wild populations.
Conservation Milestones
The Philippine Eagle is often featured in educational and conservation awareness campaigns. Despite ongoing challenges such as slow reproductive rates and shrinking habitats, conservation initiatives continue to push for stronger protection and reintroduction programmes across the Philippines.
Key Takeaways from “Philippine Eagle – One of the Largest Raptors on Earth”
| S. No. | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1 | The Philippine Eagle (Pithecophaga jefferyi) is one of the world’s largest and most powerful raptors. |
| 2 | It is endemic to the Philippines and occurs only on Luzon, Mindanao, Samar, and Leyte. |
| 3 | The species is listed as Critically Endangered with fewer than 500 mature birds left in the wild. |
| 4 | Philippine Eagles require large forest territories and are threatened by deforestation and habitat loss. |
| 5 | Conservation efforts include habitat protection, breeding programs, and anti-poaching measures. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the scientific name of the Philippine Eagle?
The scientific name of the Philippine Eagle is Pithecophaga jefferyi. It belongs to the family Accipitridae.
2. Why is the Philippine Eagle called the “Monkey-Eating Eagle”?
It was historically believed to prey mainly on monkeys. However, its diet also includes flying lemurs, snakes, birds, and other small mammals found in rainforest ecosystems.
3. What is the conservation status of the Philippine Eagle?
The Philippine Eagle is listed as Critically Endangered by the IUCN due to habitat destruction, hunting, and its slow reproductive rate.
4. In which country is the Philippine Eagle found?
It is endemic to the Philippines and occurs mainly in Luzon, Mindanao, Samar, and Leyte.
5. Why is the Philippine Eagle important in ecology?
As an apex predator, it maintains ecological balance by regulating populations of prey species. It is also considered an indicator species for rainforest health.
6. What are the major threats to the Philippine Eagle?
Deforestation, illegal hunting, habitat fragmentation, and human encroachment are the primary threats.
7. Why is this species important for competitive exams?
Questions may appear under Environment & Ecology, Biodiversity, IUCN Red List species, Endemic species, and Conservation efforts in Prelims and State PSC examinations.
8. Which organization works for its conservation?
The Philippine Eagle Foundation is actively involved in research, captive breeding, and habitat protection.
Some Important Current Affairs Links