The Former Name of Thailand and its Historical Significance
Introduction: The Evolution of Thailand’s Name
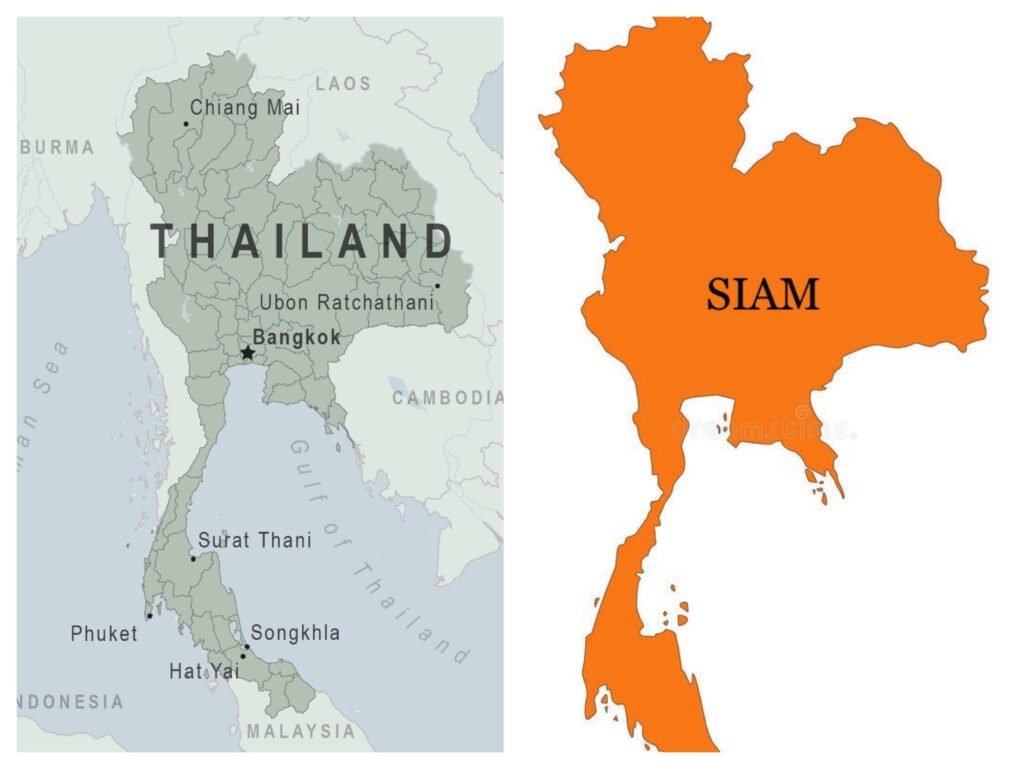
Thailand, a country in Southeast Asia, has undergone several changes in its official name throughout history. Known for its rich culture, history, and strategic location, the country was originally called “Siam” until 1939, when it was officially renamed Thailand. This article delves into the historical context of Thailand’s name change and its significance.
The Name “Siam”: Origin and Usage
Before becoming Thailand, the country was known as “Siam.” The term “Siam” was widely used in international references and was the name the country used to identify itself in global affairs. Historically, Siam was a region inhabited by various ethnic groups and was known for its royal traditions, vibrant culture, and trade networks. The name “Siam” was in use for several centuries, with its origins rooted in ancient civilizations.
Why Thailand Changed Its Name to ‘Thailand’
In 1939, a decree was passed by Prime Minister Plaek Phibunsongkhram, marking the official name change from Siam to Thailand. The change was part of a broader effort to modernize the country and create a unified national identity. The new name, Thailand, translates to “Land of the Free,” symbolizing the country’s proud history of maintaining independence in the face of colonialism. The change also reflected the growing sense of nationalism and pride in the Thai people.
Impact on International Relations and National Identity
The name change from Siam to Thailand had a significant impact on the country’s international relations. It strengthened national identity and pride while also signaling the country’s intention to modernize. The change to Thailand was not just a political move but a cultural one, emphasizing unity and the shared heritage of the Thai people. Over the years, the name Thailand has become synonymous with the country’s identity, culture, and history.
Why This News is Important
Understanding Thailand’s National Evolution
The renaming of Siam to Thailand is an essential event in the country’s national evolution. It represents Thailand’s transition from a kingdom with a colonial-era identity to a modern, sovereign nation. The decision to change the country’s name was a defining moment in Thai history, as it aligned the nation’s identity with its aspirations for independence and modernization. For students preparing for government exams, understanding this change provides insight into Thailand’s national development and its historical path toward becoming the Land of the Free.
Cultural and Political Significance
This name change has cultural and political significance, reflecting Thailand’s desire to establish a unified identity. Students preparing for exams related to international relations, history, and political science can benefit from knowing how such decisions shape national identity. The name change was symbolic of Thailand’s desire to distance itself from foreign influences and assert its independence. As a country with a rich cultural history, the change highlighted the importance of nationalism and pride for the Thai people.
Historical Context: Background of Thailand’s Name Change
Siam: The Kingdom’s Origins
The origins of the name “Siam” trace back to ancient times, with historical records suggesting it was first used in the 13th century. The Kingdom of Siam was a prosperous state, known for its rich culture, especially in arts, architecture, and religious practices. The name “Siam” was used for centuries to refer to the region that now comprises Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, and Myanmar. During the colonial era, Siam faced external pressures from European powers, who attempted to control parts of Southeast Asia.
The Rise of Thai Nationalism and the Name Change
In the early 20th century, as European colonial powers advanced in Southeast Asia, the Thai people began to embrace a sense of nationalism. The reign of King Chulalongkorn (Rama V) saw reforms that modernized the country and strengthened its sovereignty. In the 1930s, as Thailand faced political challenges, Prime Minister Phibunsongkhram and other political leaders sought to create a stronger national identity. The name “Thailand,” meaning “Land of the Free,” became a symbol of the country’s determination to remain independent and its desire to move beyond its colonial past.
Key Takeaways from “The Former Name of Thailand”
| S.No. | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| 1. | The official name of Thailand was “Siam” until 1939, when it was changed to Thailand. |
| 2. | The name “Thailand” translates to “Land of the Free,” reflecting the country’s pride in its independence. |
| 3. | The name change was part of a broader effort by Prime Minister Phibunsongkhram to modernize the country and unify the Thai people. |
| 4. | The name “Siam” had been used for centuries and was associated with the kingdom’s cultural heritage and colonial history. |
| 5. | Thailand’s name change represents the country’s transition from a colonial identity to a modern, sovereign nation. |
Important FAQs for Students from this News
1. Why was the name of Siam changed to Thailand?
The name of Siam was changed to Thailand in 1939 by Prime Minister Plaek Phibunsongkhram. The name change was part of a broader effort to modernize the country, unify the people, and assert the nation’s independence, symbolized by the term “Land of the Free.”
2. What does the name “Thailand” mean?
The name “Thailand” translates to “Land of the Free,” reflecting the country’s pride in its history of maintaining independence and its resistance against colonial powers.
3. When did Siam officially become Thailand?
Siam officially became Thailand in 1939, after the decree by Prime Minister Plaek Phibunsongkhram.
4. What was the significance of changing Siam to Thailand?
The change to Thailand helped establish a modern national identity, symbolizing unity, independence, and the nation’s departure from colonial influences. It also fostered nationalism and national pride among the Thai people.
5. How did the name change impact Thailand’s international relations?
The name change helped to strengthen Thailand’s international standing by signaling a move toward modernization and a solidified national identity. It emphasized Thailand’s sovereignty and independence during a time when many countries in Southeast Asia were under colonial rule.
Some Important Current Affairs Links